New York State Medical Treatment Guidelines for
Meniscus Injury in workers compensation patients
The New York State workers compensation board has developed these guidelines to help physicians, podiatrists, and other healthcare professionals provide appropriate treatment for Meniscus Injury.
These Workers Compensation Board guidelines are intended to assist healthcare professionals in making decisions regarding the appropriate level of care for their patients with ankle and foot disorders.
The guidelines are not a substitute for clinical judgement or professional experience. The ultimate decision regarding care must be made by the patient in consultation with his or her healthcare provider.
Description / Definition of Meniscus Injury
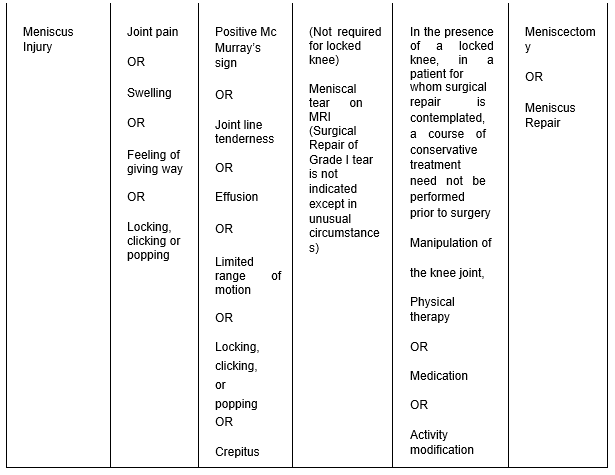
Meniscus Injury means tissue from the medial or lateral meniscus that has been torn, disrupted, or avulsed.
Mechanism of Injury for Meniscus Injury
Rotational, shearing, torsional, and/or impact traumas that cause damage to the menisci
Specific Physical Findings of Meniscus Injury
A popping, tearing, or catching sensation is described by the patient. Physical examination findings may include joint line discomfort, locked joints, or sporadic effusion. Positive results on the McMurray, Apley, Steinman (parts 1 and 2), or Childress tests may be relevant physical examination findings.
Diagnostic Testing Procedures of Meniscus Injury
- Radiographs, MRI
Radiographs, MRI are recommended in select patients as clinically indicated.
Indications: lateral, tunnel, standing Posterior/Anterior (PA), and skyline views are all radiograph types. The ultimate imaging exam is the MRI. Meniscal tear detection with MRI is sensitive and precise.
However, with asymptomatic injuries, meniscal MRI is usually abnormal. Critically noteworthy is the clinical connection between meniscus injury-specific physical exam and history results.
Because not all meniscus tears in the middle-aged and older population are related to the patients’ complaints of pain, healthcare providers should carefully assess the patient’s complaints and the presence of arthritis on the MRI when planning treatment.
Note: In particular after prior surgery, MRI arthrograms may be suitable to diagnose recurrent meniscal tears.
Non-Operative Treatment
Non-Operative Treatment is recommended in select patients as clinically indicated.
Note: For a locked knee, manipulation may be tried out. Within two to three treatments, the clinical response should be seen.
Surgical Indications / Operative Treatment
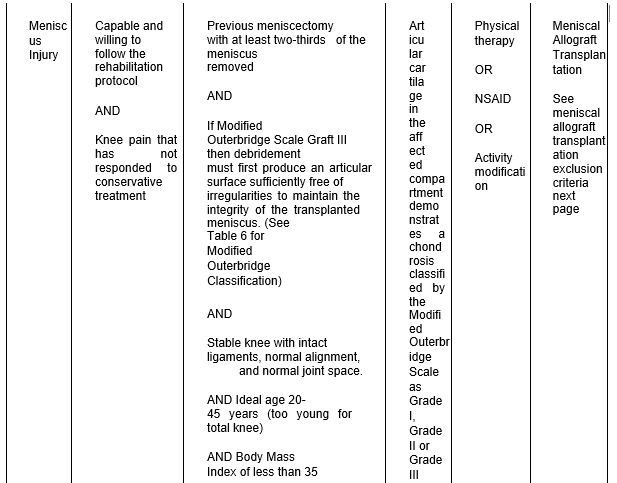
- Meniscal Allograft Transplantation
Meniscal Allograft Transplantation is recommended in select patients, as clinically indicated.
- Post-Operative Therapy, bracing
Post-Operative Therapy, bracing is recommended in select patients as clinically indicated.
Table 5: Meniscus Injury
What our office can do if you have workers compensation injuries
We have the experience to help you with their workers compensation injuries. We understand what you are going through and will meet your medical needs and follow the guidelines set by the New York State Workers Compensation Board.
We understand the importance of your workers compensation cases. Let us help you navigate through the maze of dealing with the workers compensation insurance company and your employer.
We understand that this is a stressful time for you and your family. If you would like to schedule an appointment, please contact us so we will do everything we can to make it as easy on you as possible.
I am fellowship trained in joint replacement surgery, metabolic bone disorders, sports medicine and trauma. I specialize in total hip and knee replacements, and I have personally written most of the content on this page.
You can see my full CV at my profile page.