Diagnosis of Sciatica
Sciatica is the pain in the lower back or buttocks radiating to the lower leg due to compression or irritation of the Sciatic nerve or the nerve roots (L4 to S3). The pain may be followed by a feeling of numbness and tingling in the legs. There may be symptoms of weakness in the lower extremities and the patients may complain of loss of sensation.
The diagnosis of Sciatica can be made by a physician by mere clinical examination. The majority of patients improve through conservative measures and imaging is not immediately necessary.
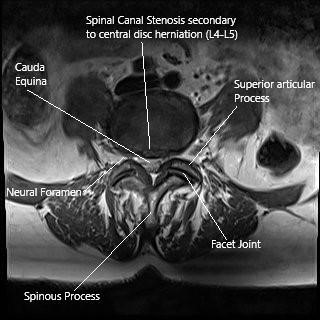
MRI of the Lumbar spine in axial section central disc herniation.
Suspicion of Sciatica
Sciatica is suspected when the pain is on one side of the leg and is more than the low back pain. The pain commonly radiates down on the back of the leg. The radiation of the pain is generally below the knee. The presence of numbness and tingling in the involved leg along with neurological findings and positive special tests help the physician to diagnose Sciatica.
History
At the doctors’ office, the physician may extract a thorough history regarding the symptoms and the events preceding the symptoms. Some of the questions the physician may ask are:
- Where do you feel the pain?
- When did the pain start?
- Did the pain start suddenly or insidiously?
- Did any activity precede the onset of pain?
- Is the pain getting worse or better?
- What makes the pain get worse and what makes it better?
- On a scale of 0 to 10 with 10 being the maximum, how would you rate your pain?
- How would you describe the character of your pain?
- Is there any associated tingling sensation in the legs?
- Do you feel any weakness or loss of sensation in the legs?
- Are you able to feel the toilet paper on your bottom?
- Any bowel or bladder incontinence?
- Did any medications help you with the pain?
- Does walking uphill or downhill change the intensity of pain?
- Do you need to stop when walking because of pain?
- Any association of symptoms with coughing, sneezing or bearing down efforts.
Besides these questions, the physician will get a history of the patient’s past medical illness, medications and allergies, and any relevant family history.
The symptoms of Sciatica as a result of a herniated disc usually get worse on sitting, coughing, sneezing, and bearing down efforts.
The nerve root compression secondary to spinal stenosis may get worse with bending backward and walking downhill. Additionally, patients may experience neurological claudication symptoms which are a pain in the legs on walking that is relieved on rest and bending forward.
Physical examination
After the evaluation of the history of the symptoms, the physician conducts a thorough physical examination. The physician looks for motor power in the muscles supplied by the Sciatic nerve to locate the nerve root involved.
To look for L3 nerve involvement, the physician checks the power of the muscles in the inner side of the thigh. The L4 nerve root is checked by the resistance offered on trying to bend the knee. Additionally, a decreased patellar reflex may point towards L4 involvement.
The physician may ask the patients to walk on their heels to look for involvement of the L5 nerve root. Additionally, the physician may test the L5 nerve root by asking the patients to extend the great toe under resistance or to move the leg outward under resistance while laying on the one side.
The physician looks for the strength of muscles supplied by the S1 nerve root by asking the patients to walk on their toes. The Achilles‘ tendon reflex may be diminished with S1 nerve root involvement.
Besides the motor power, the physician looks for sensory input from different dermatomes in the lower extremities and the saddle area. Provocative tests may be done in the form of a straight leg raising test. Various modifications of straight leg tests may make the findings more sensitive and specific.
The walking pattern of the patients is carefully examined to look for weakness in any muscle groups that may change the natural walking pattern.
Imaging
Radiological tests are usually not required for the diagnosis of Sciatica. Radiological tests are done only if there is no improvement of symptoms in 12 weeks or if there are progressive symptoms. Loss of bowel and bladder control is a surgical emergency and the patients are operated on within 48 hours to prevent permanent damage.
An X-ray is usually the first radiological investigation done in a case of Sciatica. The X-ray provides information on the bony structure of the lumbar spine in different views. Bone spurs may be found on an X-ray that may be impinging a nerve root.
A CT scan provides a much clearer image of the bony structures as compared to an X-ray. Additionally, a dye may be injected to differentiate the bony structures and the soft tissue structures.
An MRI is the radiological imaging of choice to diagnose the nerve root compression and the soft tissue structures in the spine. Electromyography (EMG) studies may be done to diagnose the nerve root compression and to localize the site of compression.
Do you have more questions?
Can sciatica cause knee pain?
Sciatica pain is usually radiated along the back or the side of the thigh and knee into the leg. Occasionally, patients may present with a confusing picture of knee problem, but maybe having sciatica. A thorough history and examination by the physician as well as diagnostic tests in the form of x-rays and MRI may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
How to fix sciatica nerve pain?
Sciatica nerve pain can be relieved to various modalities. To start with, antiinflammatory medications like ibuprofen, naproxen or Tylenol may help. If pain is not relieved with the medications, physical therapy, chiropractor and acupuncture may also help. The patient may also take medications including gabapentin or pregabalin for pain relief.
The patient should take a short period of bed rest for a day or two. The patient should continue to do normal usual activities. If the pain is not relieved, he should see his doctor. Epidural injection or nerve root blocks may help in relieving the sciatica pain. Patients who are not having any relief with any of the above-mentioned treatment plans, may need an MRI for confirmation of diagnosis and possibly surgery to relieve their pain.
How do you diagnose sciatica?
Sciatica is a clinical diagnosis, which can be corroborated by imagings with or without nerve conduction/EMG studies. Typical patient will present with pain radiating down one leg along the back or the side of the thigh index. They may have been associated with tingling and numbness or back pain.
Occasionally, patients may have weakness in the toes or the ankle. Once the clinical diagnosis is made, confirmation can be done using x-rays and MRI. In patients who have a confusing picture due to underlying comorbidity or atypical presentation, nerve conduction study and electromyographic study can be done to further confirm or rule out sciatica.
Is heat or ice better for sciatica?
Heat is usually better in patients who have sciatica, though patients who are not relieved with heat should also try ice or occasionally rhythmic use of heat and ice, cyclic use of heat or ice may help better than one alone.
Does massage help sciatica?
Massage is one of the modalities of adjuvant therapy for sciatica can be helpful and can decrease pain by strengthening the muscles as well as stretching the nerves. Deep massage can also help decrease the muscle spasms that develop in patients with sciatica.
Where to put an ice pack for sciatica?
For sciatica, an ice pack or even a heating pad can be used by placing it into the lower back and the gluteal region. It helps decrease the inflammation of the nerve there and thereby decreasing the pain and associated symptoms.
Does the inversion table help sciatica?
Inversion table similar to traction helps sciatica by increasing the height of the disk and thereby allowing the disk to go back into space thereby decreasing the compression of the nerve root may help in decreasing the pain of sciatica. The issue of inversion table as well as traction is that this is effective until the patient uses them and once the patient is upright and moving, the effect of the inversion table or the traction may not be persistent.
Can the sciatica cause ankle pain?
Sciatica or lumbar radiculopathy causes pain radiating from the back or the hip into the lower extremities down the leg. The pain radiates along the back or the side of the thigh and leg and radiates down foot. An isolated ankle pain may not be caused by radiculopathy. If the pain is on outer or inner side of the ankle and is radiating down or coming from the top then it may be associated with sciatica or lumbar radiculopathy.
Does sciatica get worse before it gets better?
90% of patients with sciatica will eventually get better in a period of four to six weeks. During this time, the pain may worsen also or it may keep on improving. Patients who have severe pain with or without tingling or numbness usually will need medical attention to relieve their pain during this duration. The treatment may involve medications, physical therapy and cortisone shots. Patients who have sudden onset of neurological deficit or weakness or worsening of the neurological deficit may need surgery also.
Can stress cause sciatica?
Sciatica like any other neurologic pain can have relation with the mental status and cognitive functions of the person. Though stress may directly not be the causative factor for sciatica, it may have its effect on the severity as well as course of the disease process of sciatica. Patients with high stress levels may have difficulty coping with sciatica and may take longer time to get better.
What happens if sciatica left untreated?
Sciatica in most patients will get better by itself in a period of four to six weeks. The pain as well as tingling and numbness tend to improve over time, though it may have periods of worsening. Patients may need treatment in the form of medications or injections to relieve the pain, so as to spend this period of four to six weeks, till then the relief is evident.
Occasionally in about 10% of the patients, there will be no relief, worsening or recurrence of sciatica pain despite all treatment modalities over four to six weeks. These patients may need surgical management to relieve their pain due to the pressure over the nerve roots.
Can sciatica be a serious disorder?
Sciatica is usually self limiting in 90% of patients and only needs treatment in the form of medication and physical therapy and occasionally cortisone injection. In about 10% of patients, this may not be relieved by any modality and these patients may need to undergo surgical treatment.
Sciatica can also rarely lead to rapid neurological deficit presenting in the form of cauda equina syndrome, which can be potentially disabling. The neurological deficit caused due to cauda equina syndrome may be permanent especially if not treated early in the disease process. Such patients may not only have weakness in their legs, but may also lose control over their bowel and bladder, which may or may not recover over time.
What are the medication that can help sciatica?
Sciatica pain can be relieved by the help of anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen, naproxen. It can also be helped by Tylenol. Stronger pain medications like tramadol and narcotic medications may occasionally be needed for a short period of time.
Neuromodulator medications like gabapentin and pregabalin may also be helpful in decreasing the sciatica pain. Occasionally, medications like amitriptyline, duloxetine and carbamazepine may also be used in some patients to relieve their pain.
Is the back brace helpful for sciatica pain?
Back brace may be helpful in patients who have back pain with or without sciatica. Patients who have only radicular pain in their lower extremity may not be helped by the back brace. Use of back brace for a long period of time may be detrimental by causing atrophy of the back muscles.
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.

