Microdiscectomy in Pregnancy
Overview
Low back pain is a common complaint in pregnancy. There may be symptoms of sciatica along with low back pain. Sciatica symptoms are usually caused by herniation of an intervertebral disc. The management is usually nonsurgical and elective surgical management is postponed after childbirth.
However, progression to cauda equina syndrome or neurological deficit may need urgent surgical intervention. Microdiscectomy surgery may be used to decompress the spine and provide relief from sciatica symptoms.
Low back pain in pregnancy has been attributed to relaxation of the ligaments caused by the pregnancy hormone relaxin. The laxity of the ligaments may lead to increased motion in the lower spine segment. Further, the weight gain in pregnancy along with the enlarged uterus causes the center of gravity to move forward from the lower spine. These all biomechanical changes in pregnancy may lead to intervertebral disc herniation.

Axial section of lumbar spine MRI.
The herniated disc may compress the spinal nerve roots and lead to radiculopathy. Lumbar radiculopathy or sciatica may present with symptoms of radiating buttock and leg pain. The pain may be associated with numbness and tingling.
The sciatica symptoms are managed non surgically in both pregnant and non pregnant females. Only patients with progressive motor weakness and cauda equina syndrome need surgical treatment.
Severe compression of the dural sac may cause cauda equina syndrome. Cauda equina syndrome may present with lower extremity weakness along with bowel and bladder incontinence.
The diagnosis of sciatica in pregnancy is made clinically by the physician. Radiological studies such as x-ray are avoided in pregnancy. MRI is generally safe in pregnancy but is only done in case of worsening motor/sensory weakness and during planning of the surgery. X-ray may be done if the benefits outweigh the potential risks.
Medical treatment is usually limited to acetaminophen (Tylenol). Nonsteroidal anti inflammatory medications and steroid medications are avoided in the first trimester (12 weeks). Other non surgical treatments such as postural correction, physical therapy and heat/cold therapy are also recommended.
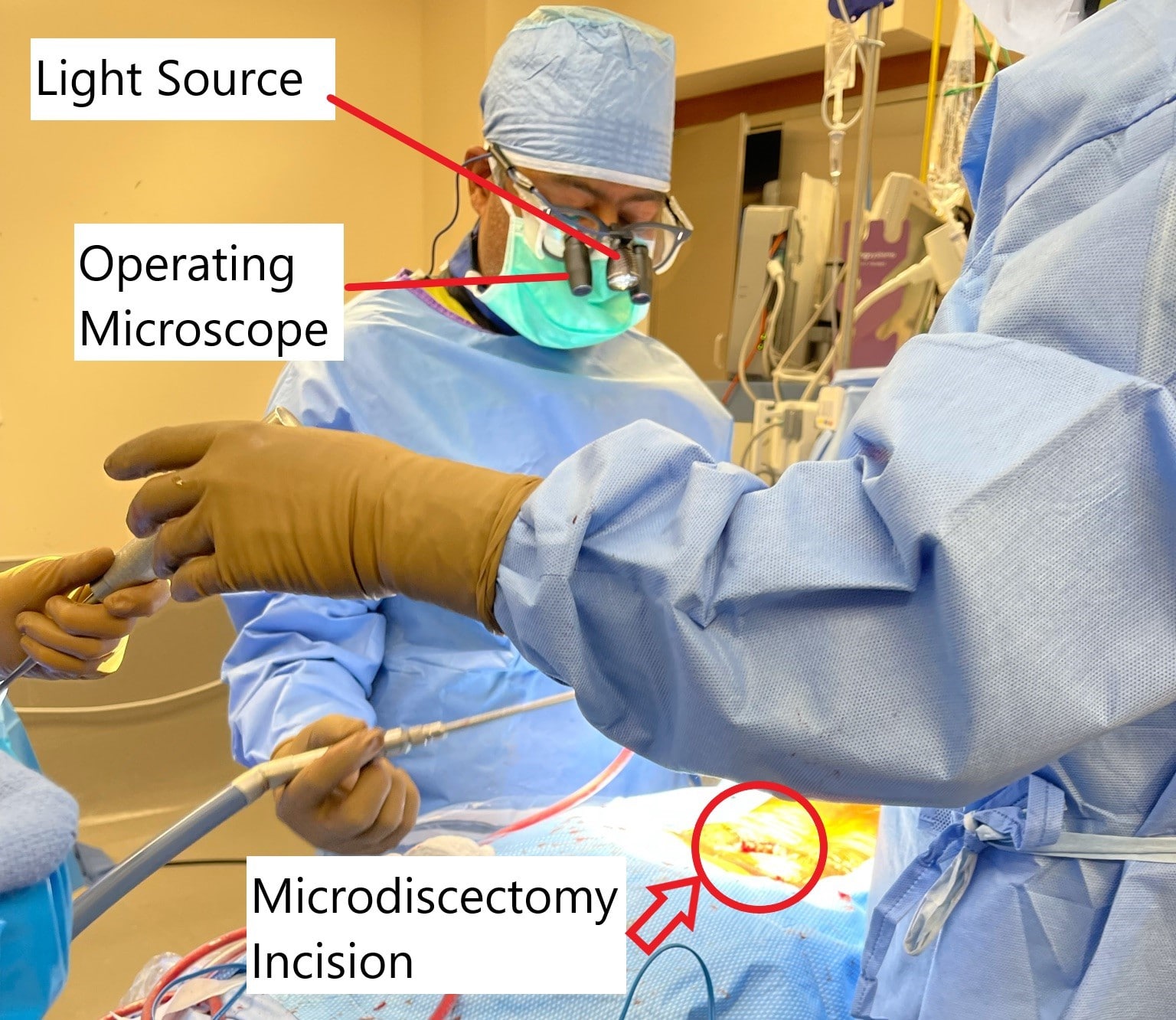
Intraoperative image showing microdiscectomy surgery.
Patients with progressive motor weakness may need surgery such as microdiscectomy to decompress the spinal segment. The surgery is usually done in the second trimester. General anesthesia is considered safe in pregnancy. Special precautions may be needed for positioning during the surgery to prevent excessive pressure on the uterus.
The surgery involves a small incision in the lower back and use of an operating microscope to magnify the incision. The surgeon then removes a small part of the lamina and then proceeds to remove the herniated intervertebral disc. The incision is closed in layers and a small bandage is applied.
The patients may need monitoring and overnight stay at the hospital. The post operative rehabilitation after microdiscectomy is the same as of non pregnant patients. The patients may need safe analgesics after surgery to help with post operative pain.
The decompress achieved with microdiscectomy leads to an excellent recovery from sciatica symptoms. Microdiscectomy in pregnancy like all other elective surgeries are generally avoided unless delay of surgery may lead to permanent neurological damage.
Microdiscectomy may be associated with complications both during and after the surgery. During the surgery there may be complications of excessive bleeding, neural damage, dural sac rupture. There may be additional rare complications of surgery in pregnancy that may cause premature labor or premature rupture of membranes. After the surgery, there may be complications of infection, epidural fibrosis and failure of discectomy.
Microdiscectomy surgery is a safe procedure when indicated in pregnant females. The complications from microdiscectomy are rare but extra care is needed both in diagnosis and surgery to prevent any side effects to the growing fetus.
Do you have more questions?
What are the risks of microdiscectomy for the fetus?
Risks to the fetus are minimal but can include premature labor or premature rupture of membranes. Careful monitoring and specific surgical precautions help mitigate these risks.
Is microdiscectomy safe during pregnancy?
Microdiscectomy is generally considered safe during pregnancy, particularly in the second trimester. Special precautions are taken to ensure the safety of both the mother and the fetus.
When is the best time during pregnancy to have microdiscectomy?
The second trimester is usually the best time to perform the surgery, as it balances the risk of teratogenicity in the first trimester and the risk of preterm labor in the third trimester.
What are the indications for microdiscectomy during pregnancy?
Microdiscectomy is indicated if there is progressive motor weakness, cauda equina syndrome, or severe pain unresponsive to conservative treatments.
Can I have an MRI during pregnancy to diagnose sciatica?
Yes, MRI is generally safe during pregnancy and is used when necessary to diagnose and plan for surgery, particularly if there are worsening neurological symptoms.
What are the non-surgical treatment options for sciatica during pregnancy?
Non-surgical treatments include acetaminophen, physical therapy, postural correction, and heat/cold therapy. NSAIDs and steroids are avoided, especially in the first trimester.
Will I need general anesthesia for microdiscectomy, and is it safe during pregnancy?
Yes, general anesthesia is typically used for microdiscectomy and is considered safe during pregnancy with appropriate precautions.
How will the surgery be performed to avoid harm to my baby?
Special positioning techniques are used to avoid excessive pressure on the uterus, and the surgical team takes extra precautions to minimize risks to the fetus.
Will I need to stay in the hospital after the surgery?
Yes, an overnight stay for monitoring is typical to ensure both maternal and fetal well-being post-operatively.
What are the potential complications of microdiscectomy during pregnancy?
Potential complications include excessive bleeding, neural damage, dural sac rupture, infection, epidural fibrosis, and failure of discectomy. Pregnancy-specific complications may include premature labor or rupture of membranes.
What pain medications can I take after microdiscectomy during pregnancy?
Post-operative pain is usually managed with acetaminophen, as other analgesics like NSAIDs are generally avoided during pregnancy.
Can I continue with my prenatal care after surgery?
Yes, you can and should continue with your regular prenatal care. Communication between your obstetrician and surgeon is essential for comprehensive care.
How long is the recovery period after microdiscectomy during pregnancy?
Recovery is similar to that in non-pregnant patients, with most patients experiencing significant relief from sciatica symptoms within a few weeks. Full recovery may take several weeks to months.
Will I need special follow-up care after microdiscectomy during pregnancy?
Follow-up care will involve both your orthopedic surgeon and obstetrician to monitor your recovery and ensure the health of your pregnancy.
What activities should I avoid during recovery from microdiscectomy while pregnant?
Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or twisting. Follow your surgeon’s recommendations for activity limitations and gradually increase your activity level as guided by your physical therapist.
Can microdiscectomy affect my ability to have a natural delivery?
Microdiscectomy itself does not typically affect the mode of delivery, but your obstetrician will consider your overall health and recovery in making delivery plans.
Can I breastfeed after having microdiscectomy?
Yes, you can breastfeed after the surgery. Ensure that any pain medications prescribed post-operatively are safe for breastfeeding.
How successful is microdiscectomy in relieving sciatica symptoms during pregnancy?
Microdiscectomy is highly successful in relieving sciatica symptoms, with most patients experiencing significant pain relief and improvement in neurological function.
What should I do if my sciatica symptoms return after surgery during pregnancy?
Contact your surgeon if symptoms return. Further evaluation may be needed to determine the cause and appropriate management.
Can I travel after having microdiscectomy while pregnant?
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.

