Dural Tears
Dura is the thin outer lining, covering the spinal cord and nerve roots in the spine. It is continuous with the covering in the brain. The dura keeps the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from leaking out. CSF is necessary for the nutrition of the brain, spinal cord, and nerve roots. If it leaks out then it will lead to decreased fluid inside the brain, which can then lead to headaches and in severe cases cause brain stem herniation.
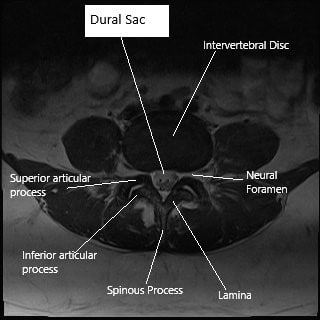
Axial section (MRI) of lumbar spine showing dural sac.
It is exposed during the spine surgeries and can inadvertently be cut or injured during the surgery. Dura may also be incised as a part of the surgery on the spinal cord or nerve roots. In either case, the dural tear needs to be repaired in a watertight fashion to avoid the leakage of the fluid from inside.
Dural Tears in Spine Surgery
Dural tears can occur during spine surgery, particularly in procedures involving the lumbar spine. These tears can be inadvertent, resulting from surgical instruments, or deliberate, as part of a planned procedure. Regardless of the cause, a dural tear requires prompt attention to prevent CSF leakage and associated complications.
Managing Dural Tears
Management of dural tears involves several steps:
Early Identification: Recognizing a dural tear early is critical. Surgeons must be vigilant for signs of CSF leakage during and after surgery.
Repair Techniques: The primary method of repair is direct suturing using fine sutures and magnification tools. When direct suturing is not feasible, synthetic grafts and other materials may be used.
Intraoperative Monitoring: Techniques such as the Valsalva maneuver help ensure the integrity of the repair. These methods are crucial for detecting any leaks and confirming that the repair is watertight.
Postoperative Care: Patients with dural tears require careful monitoring and bed rest to prevent CSF leaks. Gradual mobilization helps ensure a smooth recovery.
Dural-tear Indication
Dural repair is performed whenever there is a dural tear: inadvertently or planned. Sometimes, the dural tear may not be evident at the time of surgery and the patient may have symptoms of CSF leakage after the surgery. Such patients are initially treated without surgery by bed rest and fluids along with pain medications. If it does not get better then surgery may be needed to explore the dural tear and repair it.
Dural-tear Procedure
Dural repair is done by the use of very fine sutures and instruments. The use of magnification by microscope or loop is necessary, a watertight seal is always attempted. The repair is secondarily strengthened by the use of additional synthetic material. Occasionally, a dura may not be repairable. In this case, local or synthetic grafts are needed. Dural repair is checked by performing the Valsalva maneuver with the help of the anesthesiologist.
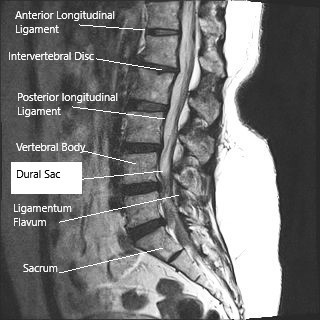
Sagittal section (MRI) of the lumbar spine showing dural sac.
Dural-tear Post-surgery Recovery
The patients with dural tear need to be on bed rest. They are gradually weaned out of bed rest to check if they do not develop symptoms of CSF leak in the form of headaches. Most of the patients usually do very well and there is no difference between the recovery of patients with or without a dural tear.
Result and Prognosis
A dural tear is an inadvertent complication of spine surgery. They have repaired primarily or secondary and patients do well after the surgery.
Conclusion
Dural tears, though a common complication in spine surgery, can be effectively managed with prompt and precise repair techniques. Advances in surgical methods and materials continue to improve patient outcomes, ensuring that most patients recover well with minimal complications. Understanding the role of the dura, the impact of CSF leaks, and the importance of meticulous repair techniques is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients undergoing spine surgery. By combining general knowledge about the dura with insights from recent studies, we can enhance our approach to managing this complication and improve the overall success of spine surgeries.
Do you have more questions?
What is the function of the dura in the spine?
The dura mater is a protective membrane that surrounds the spinal cord and nerve roots, maintaining the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) which cushions and nourishes these structures.
What are the common causes of dural tears during spine surgery?
Dural tears can be caused by inadvertent injury from surgical instruments, excessive retraction of tissues, or as a planned part of certain surgical procedures.
Why is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) important?
CSF provides essential nutrients to the brain and spinal cord, acts as a cushion to protect against injury, and helps remove waste products from the central nervous system.
How are dural tears detected during surgery?
Dural tears can be detected by observing clear fluid leakage, using magnification tools, and performing tests like the Valsalva maneuver to identify any breaches.
What are the symptoms of a dural tear if it is not immediately detected during surgery?
Symptoms can include severe headaches, nausea, and sometimes clear fluid drainage from the surgical site, indicating a CSF leak.
How is a dural tear repaired during surgery?
Dural tears are repaired using very fine sutures and instruments under magnification to ensure a watertight seal. Synthetic grafts may be used if direct suturing is not feasible.
What materials are used if the dura cannot be directly sutured?
Synthetic grafts or local tissue grafts are used to reinforce or replace damaged dura, ensuring a watertight seal.
What is the Valsalva maneuver, and how is it used in dural repair?
The Valsalva maneuver involves the patient holding their breath and straining, which increases pressure in the thoracic and abdominal cavities, helping surgeons identify leaks in the dura.
What postoperative care is required for patients with dural tears?
Patients need to be on bed rest initially to monitor for CSF leaks. Gradual mobilization is attempted to ensure no recurrence of symptoms, with close follow-up care.
What are the long-term outcomes for patients who have had dural tears repaired?
Most patients recover well without significant long-term complications if the tear is promptly and properly repaired.
Can dural tears lead to serious complications if not managed properly?
Yes, if not managed properly, dural tears can lead to persistent CSF leaks, headaches, infections, and in severe cases, brain herniation.
Are there any preventive measures to avoid dural tears during spine surgery?
Surgeons can minimize the risk by using meticulous surgical techniques, employing advanced imaging, and ensuring proper instrument handling.
What role does magnification play in repairing dural tears?
Magnification, through microscopes or surgical loops, helps surgeons accurately suture the delicate dura and ensure a watertight repair.
How does a dural tear affect the recovery process compared to a surgery without complications?
Recovery may require additional bed rest and monitoring, but with proper management, long-term recovery is usually comparable to surgeries without complications.
What advancements in dural repair techniques are discussed in recent studies?
Recent advancements include the development of new suturing techniques, synthetic graft materials, and improved intraoperative monitoring methods.
Can dural tears recur after initial repair?
Recurrence is rare if the initial repair is successful, but ongoing symptoms or new CSF leaks should be promptly evaluated.
What are the signs of a successful dural repair?
Signs include the absence of CSF leaks, resolution of headaches, and normal neurological function without additional complications.
How is a CSF leak managed if it occurs after the patient has been discharged?
Management includes bed rest, hydration, and sometimes additional surgery to repair the leak if conservative measures fail.
How does bed rest help in the recovery of a dural tear?
Bed rest helps reduce pressure on the dura and allows time for the repair to heal, minimizing the risk of CSF leaks.
Are there specific risks associated with synthetic grafts in dural repair?
Risks include infection, rejection, and potential for the graft not integrating properly, although these are generally low with modern materials.
What follow-up care is necessary after a dural tear repair?
Follow-up care includes regular check-ups, monitoring for symptoms of CSF leaks, and ensuring the patient avoids activities that could stress the repair site.
What are the potential complications of a dural tear repair surgery?
Potential complications include infection, persistent CSF leaks, and neurological deficits, although these are uncommon with proper surgical technique.
Can dural tears be completely avoided during spine surgery?
While the risk can be minimized with careful surgical technique, dural tears cannot be completely avoided due to the complexity of spine surgeries.
How long does it typically take to recover from a dural tear repair?
Recovery time varies but generally spans a few weeks to a few months, depending on the severity of the tear and the patient’s overall health.
I am Vedant Vaksha, Fellowship trained Spine, Sports and Arthroscopic Surgeon at Complete Orthopedics. I take care of patients with ailments of the neck, back, shoulder, knee, elbow and ankle. I personally approve this content and have written most of it myself.
Please take a look at my profile page and don't hesitate to come in and talk.

