Cervical Laminoplasty: A Novel Surgery
If neck pain worsens and interferes with daily activities, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider. At Complete Orthopedics, our expert team is committed to treating neck injuries using tailored approaches and surgical methods. We strive to understand your symptoms, identify the underlying causes, and recommend suitable treatments or surgeries.
Our facilities are spread across New York City and Long Island, affiliated with six top hospitals, ensuring high-quality neck care. You can schedule an appointment with our orthopedic experts online or by phone. Learn about the causes and treatments for neck pain and discover when surgery is the best option.
Overview
Cervical laminoplasty is one of the newer and novel surgical procedures done on the neck for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. This surgery is performed from the back of the neck. This surgery is done in patients who have weakness due to compression of the spinal cord in the neck.
Laminoplasty is a non-fusion surgery, which means that it does not lead to restriction of movement of the neck as opposed to fusion surgeries that cause restriction of the movement of the neck. It gives excellent results in appropriately chosen patients.
Indications
Cervical Laminoplasty is performed in patients who have spinal cord compression at multiple levels in the neck. These patients may have compression of the spinal cord due to wear and tear and aging changes. Some patients may also have underlying cervical spine stenosis These patients with stenosis have a smaller diameter of the spinal canal. Patients with congenital spinal canal stenosis are at higher risk of developing spinal cord compression and its subsequent complications.
An ideal patient for laminoplasty is one who does not have any neck pain or any pain going down into the arm (cervical radiculopathy). These patients have a good contour of their neck (Cervical Lordosis) and are not found to have any gross instability of the neck.
Prior imaging of the neck and sometimes the whole spine is done before the surgical treatment is planned. X-rays, MRI, and CT scans are performed to find the right candidate as well as do good surgical planning. Occasionally, the patient may have to undergo EMG and nerve conduction study before surgery to confirm the diagnosis.
These patients usually have weakness in their legs, which manifests in the form of gait problems and imbalance. These patients may also have weakness in their hand and upper extremity. Occasionally, thereby the patients who have more weakness in their upper extremity than their lower extremity as is the presentation of central cord syndrome.
Patients who have pain in one or both upper extremities only are not a good candidate for the surgery. Also, patients who have an inflammatory disease of their neck including ankylosing spondylitis or rheumatoid arthritis are not good candidates for this type of surgery.
Patients who have weakness along with pain in one or both arm can be a candidate for the surgery along with decompression of their nerve root, which can be done at the same time.
Cervical Laminoplasty Operative Technique
Laminoplasty is done under general anesthesia and an endotracheal tube is passed into the patient’s windpipe to maintain the ventilation during the surgery. We also use spinal cord monitoring by the use of electrodes and monitoring the sensory and motor functions of the nerves during the surgery. This helps in knowing if something is going bad with the nerve or the spinal cord during the surgery and helps us do the procedure safely.
Patient is positioned prone on their belly on the operating table and their head is fixed. The hairs from the back of the head are shaved. The shoulders are taped to the bed. We use intraoperative imaging to confirm our levels and treatment.
The surgical incision is given in the midline on the back of the neck and the back of the spine is exposed with meticulous dissection and control of bleeding. This surgery involves opening up the spinal canal from the back thereby giving space for the spinal cord and relieving the compression from the spinal cord.
The compression is usually from the front of the spinal cord. In patients who have a good neck contour, the surgery allows the spinal cord to move back. This drifting of the spinal cord towards the back relieves it off the pressure.To open the spinal canal, the lamina of the back of the spine is cut sequentially over multiple levels on one side.
This cut is through-and-through into the spinal canal. A similar cut is made on the lamina on the other side but is not through-and-through. This allows hinging the spinous process onto another side of lamina. Once the hinging is done, the spinal canal opens on the one side.
This opening is kept in place by the use of plate and screws. Many plates and screws can be used in the fixation. This opening of the canal allows the spinal cord to drift back and relieve its pressure.
Once it is done, the spinal cord is meticulously examined and all the bleeding is controlled. If the patient has radicular pain also then foraminotomy to relieve the pressure from the nerve root can also be performed at the same time. The incision is closed.
We regularly use vancomycin antibiotic powder to prevent infection and allow good healing. Patients are put in a cervical collar for a couple of weeks for comfort
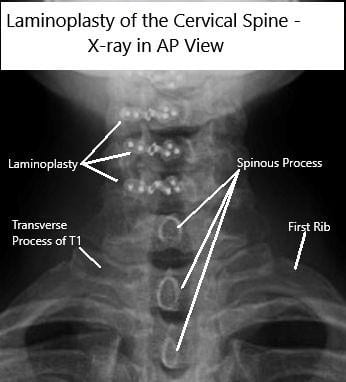
AP and Lateral view X rays of Laminoplasty C3-6
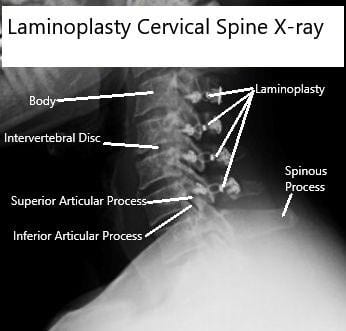
AP and Lateral view X rays of Laminoplasty C3-6
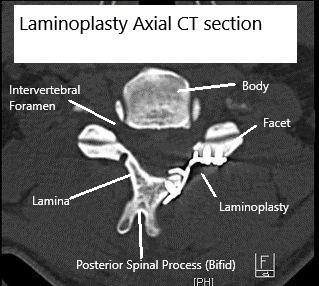
Axial CT scan Post-op Laminoplasty
Benefits and Risks
One of the primary benefits of cervical laminoplasty is the relief from symptoms like pain, numbness, and weakness, thereby improving quality of life. Unlike procedures that fuse the vertebrae together, laminoplasty preserves the natural movement of the spine, which is significant for maintaining mobility
However, like any surgery, laminoplasty comes with risks. These include bleeding, infection, nerve damage, and in rare cases, spinal cord injury. Long-term complications might include loss of spinal alignment, kyphosis (forward curvature of the spine), recurrent stenosis, and lordosis (inward curvature of the spine)
Cervical Laminoplasty Recovery
Carefully selected patients who undergo laminoplasty do well after the surgery. They recover gradually over a period of time. Occasionally, they may have to go to rehab especially if their activities are grossly limited due to their disease process. Laminoplasty allows the patient to retain and recover there range of motion.

AP and Lateral view X-ray Post-op Laminoplasty and Posterior Spinal Fusion
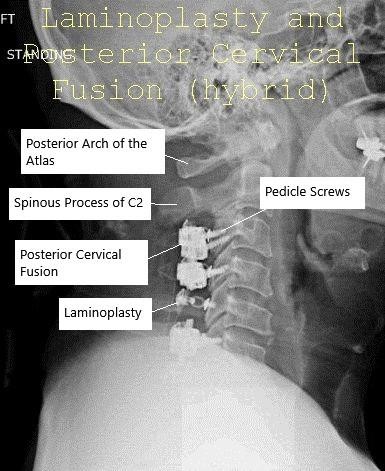
AP and Lateral view X-ray Post-op Laminoplasty and Posterior Spinal Fusion
Alternative Surgical Options
If cervical laminoplasty is not suitable, other surgical options are available. A laminectomy involves removing the lamina to decompress the spinal cord but often requires spinal fusion, limiting mobility. A laminotomy, on the other hand, involves making a small hole in the lamina to relieve pressure without removing the entire structure. Another option is an anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF), which is performed through the front of the neck and involves fusing the vertebrae. Total disc replacement (TDR) is also an option, aiming to preserve spinal motion by replacing the damaged disc with an artificial one
Long-Term Outlook
The success rate of cervical laminoplasty is promising, with studies showing that up to 70% of patients experience long-term relief from their symptoms. The outcome of the surgery depends on factors such as the patient’s overall health, age, the extent of spinal cord compression, and how long symptoms were present before surgery
Conclusion
Laminoplasties are safe surgery in appropriately chosen patients of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy with or without radiculopathy. This is a non-fusion technique, which allows patients to keep the movement of their neck intact. This surgery does not involve removal of excessive bone from the back thereby keeping the anatomy intact. Occasionally, this surgery can be also used as a hybrid procedure with foraminotomy or fusion at other levels or the same level.
Do you have more questions?
What is the typical recovery time after cervical laminoplasty?
Recovery time varies, but most patients can expect to return to light activities within a few weeks. Full recovery, including return to work and more strenuous activities, generally takes between 2 to 8 weeks, depending on the individual and the nature of their work
Will I need physical therapy after cervical laminoplasty?
Yes, physical therapy is often recommended after cervical laminoplasty to help strengthen the neck muscles, improve mobility, and ensure proper healing
How long will I need to wear a cervical collar after surgery?
The duration of wearing a cervical collar varies. It could be a few days to several weeks, depending on your specific case and your surgeon’s recommendations
What kind of pain management can I expect post-surgery?
Pain management typically involves oral medications, including painkillers and muscle relaxants. NSAIDs are usually avoided for the first six weeks to not impede the healing process
Are there any dietary restrictions post-surgery?
There are no specific dietary restrictions, but staying hydrated and consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can aid in recovery. Avoid alcohol and tobacco as they can hinder healing
Can cervical laminoplasty be performed on patients with advanced arthritis?
Cervical laminoplasty may not be suitable for patients with advanced arthritis where there is minimal motion left in the spine. Other surgical options might be more appropriate in such cases
How is cervical laminoplasty different from other spinal surgeries like laminectomy or discectomy?
Cervical laminoplasty reshapes the lamina to relieve pressure while preserving spinal motion. Laminectomy involves removing the lamina, often leading to spinal fusion, while discectomy involves removing a herniated disc
What are the signs of infection I should look out for after surgery?
Signs of infection include redness, swelling, warmth, and drainage from the incision site, as well as fever. Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you notice these symptoms
Is cervical laminoplasty a permanent solution for spinal stenosis?
While cervical laminoplasty can provide long-term relief, it may not be a permanent solution for everyone. Some patients may experience recurring symptoms or complications over time
Can cervical laminoplasty improve my range of motion?
Cervical laminoplasty aims to preserve your current range of motion rather than improve it. It prevents further loss of motion by avoiding spinal fusion
How soon after surgery can I resume driving?
You should avoid driving until your follow-up visit and you are no longer taking narcotic pain medications. Your ability to turn your head sufficiently to drive safely is also a factor
What types of activities should I avoid during recovery?
Avoid lifting anything heavier than 10 pounds, pushing, pulling, and strenuous activities. Gradually increase walking as it is beneficial for recovery
How long will I stay in the hospital after the procedure?
Hospital stays typically range from 1 to 2 nights, depending on your recovery progress and any complications that may arise
Are there long-term complications associated with cervical laminoplasty?
Long-term complications are rare but can include loss of spinal alignment, kyphosis, recurrent stenosis, and lordosis
Will cervical laminoplasty cure my neck pain completely?
While many patients experience significant relief from symptoms, there is no guarantee that pain will be completely eliminated. Success rates vary, and some patients may have residual pain
What is the success rate of cervical laminoplasty?
Success rates are quite good, with up to 70% of patients experiencing relief from symptoms for up to 10 years post-surgery. Individual results vary based on several factors
Can I engage in sports after recovering from cervical laminoplasty?
Once fully recovered and cleared by your surgeon, you may be able to return to some sports. However, activities that put significant strain on the neck should be avoided or approached with caution
Will I have a visible scar after cervical laminoplasty?
The incision is typically made in the back of the neck, and while there will be a scar, it usually fades over time. Proper incision care can help minimize its appearance
How does the surgeon decide between the open door and French door techniques?
The choice of technique depends on the specific anatomy and condition of your spine. Your surgeon will choose the method that offers the best outcome for your situation
Are there any non-surgical alternatives to cervical laminoplasty?
Non-surgical options include physical therapy, medications, and epidural steroid injections. These can be effective for managing symptoms but may not address the underlying cause as effectively as surgery
What happens if the laminoplasty doesn’t relieve my symptoms?
If symptoms persist after surgery, further evaluation is necessary. Additional treatments, including other surgical options or revision surgeries, might be considered
How should I care for my incision after surgery?
Keep the incision clean and dry, inspect it daily for signs of infection, and follow your surgeon’s instructions on changing dressings and using any prescribed ointments or medications
Can cervical laminoplasty be done as an outpatient procedure?
Cervical laminoplasty is typically performed as an inpatient procedure, requiring a hospital stay of 1 to 2 nights for monitoring and initial recovery
How does my general health affect the outcome of cervical laminoplasty?
Your general health, including factors like age, overall fitness, and the presence of other medical conditions, can significantly affect your recovery and the overall success of the surgery
What lifestyle changes should I make after cervical laminoplasty?
Post-surgery, you should maintain a healthy diet, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol, engage in regular low-impact exercise, and follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for neck care and physical therapy
I am Vedant Vaksha, Fellowship trained Spine, Sports and Arthroscopic Surgeon at Complete Orthopedics. I take care of patients with ailments of the neck, back, shoulder, knee, elbow and ankle. I personally approve this content and have written most of it myself.
Please take a look at my profile page and don't hesitate to come in and talk.

