Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion
Cervical spine discomfort is a common issue for many people, but if it worsens and starts interfering with your daily life, or if it’s accompanied by swelling, sensitivity, or inflammation, it’s crucial to seek medical help.
Located in New York City and Long Island, we have access to six hospitals and state-of-the-art facilities for advanced cervical spine surgeries and orthopedic care. Booking a consultation with an orthopedic surgeon is easy—either online or by phone.
Learn about the different causes and treatments for cervical spine pain, and recognize when surgery is the best option.
Overview
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) is the most common surgical procedure that is performed over the cervical spine or the neck. The surgery is essentially performed from the front of the neck.
Indications for Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion surgery:
The most common indication for ACDF is degenerative cervical spine disease that is aging and wear and tear of the cervical spine. This wear and tear also known as degenerative disc disease causes compression on the spinal cord or the nerve roots manifesting via multiple mechanisms including disc, osteophyte or shrinkage of the spinal canal (stenosis).
Other indications include traumatic injury to the neck through the disc with or without the involvement of facet joints. This may present in the form of fracture, subluxation, or dislocation of the spine. These injuries may present with cervical radiculopathy in the form of tingling, numbness, pain in the upper extremities. They may also present with severe spinal cord compression with quadriplegia leading to complete loss of power as well as sensation in all muscles of the extremities below the level of involvement.
These may present in the form of radiating neck pain, tingling, numbness, weakness in either extremity. It may also present with or without the involvement of balance, bowel or bladder. Patients with wear and tear usually do well with conservative treatment with the use of medications, physical therapy with or without cortisone injections.
Rarely, the patients with cervical spine disc causing compression on the spinal cord of the nerve roots may need urgent surgery without a trial of conservative management especially in cases who develop rapidly worsening neurological status, involvement of bowel or bladder, or balance with worsening. This is to prevent further worsening of neurologic status, with the hope of recovery of the deficit that has already been there.
Procedure
ACDF can be performed at one or multiple levels depending on the requirement and indication. The surgery is done usually through a transverse incision on the front of the neck onto the one side with careful dissection and retraction of vital structures. The vital structures include food pipe, windpipe as well as major vessels of the neck along with the nerves. The level of the spine to be operated is checked with the use of imaging during the surgery.
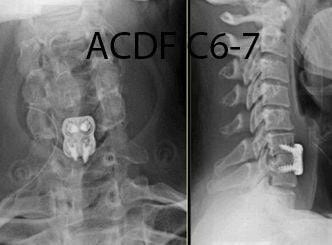
Once the level is confirmed, the disc is removed thoroughly all the way to the back. The compression over the spinal cord and/or nerve roots is removed with thoroughness. Once the compression is removed, space is filled with the spacer. This spacer can be in the form of allograft cadaveric bone or metal or polymer cage. Once space is filled, it is usually bridged with the use of a plate and screws.
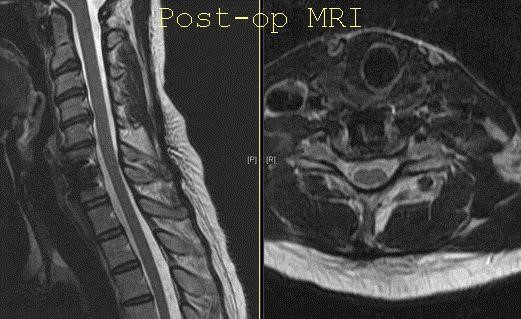
A similar procedure of cleaning the disc and filling it with the graft can be performed simultaneously at multiple levels. The spine is stabilized thereafter by the use of a plate and multiple screws. The final result is checked with imaging during the surgery.
Postoperative recovery
The patients usually stay in the hospital for 2 to 4 days and are sent home in most instances. Occasionally, the patient who is weak may need to go to the rehabilitation center for recovery. It is expected that the pain is relieved after the surgery. Tingling and numbness may take some longer time to be relieved.
Weakness may also take some time to recover after the surgery. The patients are usually in a collar and are allowed to mobilize under supervision. They are allowed to all activities of daily living. They are usually seen in the office within 2 weeks after the surgery. Physical therapy may be required for optimal recovery.
Risks and complications
As with all other surgeries, cervical spine surgery is also associated with certain risks and complications. These include injury to nearby nerves and vessels, swallowing issues, hoarseness of voice, injury to food pipe or windpipe, injury to the spinal cord or nerve roots causing temporary or permanent worsening of symptoms, failure of the implant, cage, need for reoperation, need for augmentation of fixation from the back.
Systemic complications include blindness, blood clots in the legs, neurological, pulmonary, cardiac complications, even death.
Prognosis:
ACDF is one of the common surgeries of the cervical spine with excellent results. The patients usually recover well after the surgery. The fusion usually happens over a span of 3 to 4 months and the patient is able to perform all activities of daily living right from the first postoperative day. The patient can return to the pre-surgery level of activity at 2 to 4 months depending on the type of job the patient is involved in. In skillful hands, cervical spine surgery is a relatively safe surgery with excellent results.
Conclusion
ACDF is a reliable and commonly performed surgery for treating various cervical spine conditions. It offers significant pain relief and improved function for most patients. However, it’s important to weigh the benefits against potential risks and to follow up regularly with your healthcare provider to ensure the best outcomes.
Do you have more questions?
What are the typical long-term pain management strategies?
Pain management is relatively easier after an ACDF/TDR surgery as the pain requirement is less. Patients are allowed to take narcotic medication for the initial 1 to 2 weeks as needed. Tylenol can be used to supplement the medications. After 2 to 3 weeks, patients can also take anti-inflammatory medications as needed after ACDF surgery. Patients are allowed anti-inflammatory medications sooner after a disc replacement surgery as there is no fusion involved. Anti-inflammatory mediations are known to delay bone healing.
What long-term outcome can I expect from TDR?
Once the implant settles itself into the bone of the endplates with ingrowth into the artificial disc which usually takes 3 to 6 months, the patient is almost back to normal. There is always the disc degeneration that happens due to ageing which can continue to happen at other levels. The levels adjacent to the TDR are less susceptible to such degenerative changes as compared to ACDF but may become symptomatic over time due to the natural progression of the degenerative disease process.
How does ACDF vary for older patients?
ACDF is most commonly done for degenerative disc disease, which is a commoner condition in older population than younger. As the patient gets old, the body physiology changes and any surgery becomes a moderate to high-risk surgery. The physician and the patient have to discuss the risks and the benefits of the surgery to come to a decision if they would like to go forward with the surgery or not. With regards to specific concerns, old age does cause delayed healing which may lead to nonhealing also. Also, the soft tissue healing is slow down and certain tissue are more friable than being a younger adult patient leading to a higher risk of complications including bleeding, dural tear, nonunion or nonhealing, subsidence of the cage among others. Also, if a patient of the older population has neurological deficit, the chances of them recovering is lower than a younger adult. Patients of younger population also are at higher risk with regards to anesthesia as well as postop recovery and rehabilitation.
How is ACDF approach differently for patients with multiple health issues?
Patients with multiple health issues need to be optimized medically before the surgery. If needed, they need to see their primary care doctor as well as other subspecialists that they regularly see as well as the presurgical team. If a new health condition is diagnosed, then they may need to undergo further workup and may need to see another subspecialist with an aim to optimize their health condition before the surgery. The patient’s medications also need to be managed and certain medications need to be stopped before the surgery to decrease the complications from anesthesia and surgery and allow recovery in the postop period.
Are there specific considerations for athletes undergoing ACDF?
There are no specific considerations for athletes who undergo ACDF. In the first place, if the cervical pathology can be managed without a fusion surgery, like by utilizing foraminotomy surgery hence avoiding a fusion surgery can be better for an athlete. Also, if he is a younger patient, we would consider an option of total disc arthroplasty rather than an ACDF to allow retaining movement at the disc space.
What are the gender specific considerations in ACDF?
There are no gender specific concerns in ACDF. The ACDF is done with the same approach and in the same way for either gender. We do try to put the skin incision along one of the neck creases for both genders so as to make it cosmetically more acceptable.
What genetic factors could influence the success of ACDF?
ACDF is inherently a very successful surgery with excellent outcomes. Genetic conditions which hamper or impair the immune system can lead to high risk of complications including infection and nonhealing. Also, patients who have congenital spinal stenosis may need another surgery from the back of the spine to completely relieve the pressure on the spinal cord or the nerve roots. Patients with any genetic conditions which may alter the surgical course need to be optimized, if possible, with medications before the surgery.
How does body weight impact the risk and outcomes of ACDF?
An increased body weight which also means increased BMI does increase risk of complication in any surgery including ACDF. The incidents of wound drainage are higher in patients with increased weight. The chances of a patient with increased weight having other medical problems are higher which also increases the risks of complication as discussed above. The surgery, if well indicated, can still be carried out with safe practices with excellent results.
How does prior neck surgery affect ACDF planning and outcome?
A previous neck surgery makes an ACDF a tough surgery due to the approach to the anterior cervical spine. If the patient had an extensive neck surgery previously for any reason, which leads to scar formation on either side of the neck that is the right and the left side of the neck, then it is better to avoid an ACDF surgery. Occasionally, due to the cervical pathology, it may be necessary to approach the cervical spine from the front in which case we may have to meticulously dissect the soft tissue and protect the vital structures. Rarely, we may need an ENT surgery to help approach the anterior spine. If the patient had an ACDF surgery in the past, then we can approach the neck from either the same side or the other side, approach to the ACDF also depends on the integrity of the nerve supplying the vocal cords. To find that out, the patient is sent for an ENT consult to look for mobility of the vocal cords. The patient may have an asymptomatic paralysis of vocal cord which can be diagnosed by a direct laryngoscopy by the ENT surgery. If we find that the patient has a vocal cord paralysis on the side where the previous ACDF surgery was approached, then we do the surgery from the same side and do not approach the neck from the other side fearing that if the nerve on the other side is also injured inadvertently then the patient may have high risk of respiratory complications.
What are the special considerations for patients with osteoporosis?
Patients who are diagnosed with osteoporosis before the surgery are managed with medications to optimize their bone health and improve their bone quality. If the surgery is still indicated, meticulous and efficient method is used to keep the integrity of the endplates, at the same time preparing them for fusion. Different implants may be used for such surgery. Occasionally, patients with osteoporosis may need a surgery from the back of the neck to increase the stabilization at the level so that collapse can be avoided and healing can happen
How does diabetes affect ACDF surgery and recovery?
Patients with diabetes have poor immune system and are at higher risk of infection as well as delayed or nonhealing. Optimization of blood sugar in the previous three months can help to mitigate some of these risks. Patients are encouraged to keep the control of blood sugar at a strict level in the perioperative period.
Are there specific concerns of patients with autoimmune disorders?
Patients with autoimmune disorders, who are on medications, have poor immune response due to the medication effect. They are at higher risk of infection as well as poor healing of the soft tissue as well as bone. Their health condition needs to be optimized and coordinated with their primary care doctor and rheumatologist and autoimmune expert, and patients are informed of the higher risks during and after the surgery.
How can complications be minimized?
With the use of magnified vision by using loops or operating microscope, the visualization is enhanced and it helps in decreasing the complications. Also, using appropriate instruments and retraction and the use of good team helps in minimizing the complications.
What are the signs of infection after ACDF/TDR?
Redness, swelling, discharge from the incision site, pain in the neck or in the upper chest, fever, chills, increased heart rate are few of many signs of infection after ACDF/TDR. Patient should be taken to the emergency room or informed to the doctor immediately when such things happen.
What are the most common complications of ACDF/TDR surgery?
ACDF/TDR surgery is a relatively safe surgery with a very low rate of complications. Most common complaints of patients after an Anterior cervical surgery (ACDF or TDR) are related to shoulder pain due to positioning and positioning and hoarseness of voice due to retraction. These complaints usually improve in the next 3-5 days. Occasionally patients may need medications for it. They can have dysphonia or hoarseness of voice due to retraction as well as the endotracheal tube. We tend to mitigate this by deflating and reinflating the endotracheal tube cuff so as to decrease the pressure on the vocal cords. Rarely, the recurrent laryngeal nerve, the nerve supplying the vocal cords may get stretched or pressed, in such cases patients may develop a short-term hoarseness of voice for about 4 to 6 months. This hoarseness of voice can be managed by intervention with an ENT doctor. Patients can have dysphagia or difficulty in swallowing, which gets better in the next few days or weeks. The other and usually rare complications can include wound dehiscence, infection, injury to large vessel or food pipe or windpipe, injury to the nerve supplying the vocal cord, injury to the nerve roots or the spinal cord, bleeding among others. Considering the use of magnified vision with the use of loops or microscopes, these incidences are very far and few. Not being able to heal and need for more surgery is also a complication of these surgeries.
What are the risks of spinal cord injury after ACDF/TDR?
Considering that we use magnified vision by using loops or operating microscope, the risk of spinal cord injury after ACDF/TDR is minimal to rare. Sometimes patient may have injury to the spinal cord preexisting due to the arthritis or the disc herniation showing a swelling in the spinal cord on the MRI before the surgery. Decompressing such spinal cord can possibly lead to healing of this lesion with some to full recovery of the symptoms.
What are the risks associated with anesthesia in ACDF/TDR?
Risks of anesthesia in ACDF are the usual as with any other surgery.
How are blood clots prevented during and after ACDF/TDR?
We use sequential compression devices on both calf muscles, calf area to keep the blood pumping from the legs while the patient is in the surgery or after surgery when resting. Patients are encouraged to walk around in the postoperative period which also allows to decrease the risk. Patients are started on anticoagulation prophylaxis if they are high-risk in the postop period once the risk for bleeding is minimized.
What should I do if I experience severe pain after the surgery?
Severe pain is unusual after an ACDF/TDR surgery. Patients are provided with pain medications. If the pain is not controlled with pain medications and is worsening, the patient should contact their doctor. If the doctor is unreachable, then the patient should visit the emergency room to get checked out and to rule out any infection or any other such complication.
What are the risks of nonunion or failed fusion?
The risk of nonunion is very low after a single level ACDF/TDR. If multiple levels are done, then the risk may increase. We use multiple steps to mitigate this risk by doing a good endplate preparation as well as use of local bone graft and allograft to stimulate stimulation with a good fixation to keep the rate low.
What are the implications of hardware failure?
How are dural tears handled during surgery?
Dural tears are rare during an ACDF/TDR surgery. If it is a small rent, then it can usually be packed and sealed with an artificial membrane and sealant. If the tear is big, then we may have to make a bigger cut through the bone to allow repair of the hole with sutures followed by sealing it with a membrane on the top and sealant.
How is the cervical area accessed during the surgery?
Traditionally, cervical spine can be accessed either from the front or the back. The surgery from the front is called anterior cervical discectomy or corpectomy, which is usually associated with fusion. Also, the surgery from the back is called posterior cervical approach and surgeries like posterior cervical laminectomy and fusion or laminoplasty or foraminotomies can be done through that approach. In anterior cervical approach, the skin is usually cut in a transverse manner along a skin crease which is cosmetically acceptable and a plane is developed between the throat muscles and the sternocleidomastoid muscle to reach the anterior part of the front of the cervical spine. This is relatively bloodless surgery with fast recovery and recuperation. Posterior cervical spine surgery is done with a vertical incision along the midline splitting the muscles to reach the back of the cervical spine. Posterior spinal approach is associated with a little more blood loss as compared to the anterior approach and has higher risks and complications, which include wound dehiscence, infection among others.
What type of anesthesia is used during ACDF?
General anesthesia is the usual type of anesthesia we use during ACDF in which a tube is passed into the windpipe or trachea of the patient and the anesthesia controls the ventilation of the lungs.
How are affected cervical discs removed?
The affected cervical discs are removed with the use of a variety of instruments which include a plate, curettes, pituitary rongeurs, Kerrison rongeurs. Various sized instruments are used to allow a microdissection and removal of the disc while at the same time avoiding any injury to the spinal cord or the nerve and protecting the integrity of the spine. The visualization is usually done with the use of specialized glasses which are magnified to 2.5 to 3.5 times or with the use of an operating microscope.
What materials are used for spinal fusion?
The spinal fusion for anterior cervical spine approach or ACDF uses interbody cage between the two vertebral bodies in the disc space which can be made up of fibular cadaveric bone graft or PEEK cage or a Titanium cage usually. This is supported with a plate in front of the spine, which is usually made of titanium and fixed with titanium screws.
How is fusion material secured?
To allow fusion to happen between two cervical vertebral bodies, we usually pack the space between them with a spacer which can be of an allograft, autograft, PEEK, or Titanium, which is packed with bone either from patient’s body or from a cadaver or a mixture of the two and the structure is held together with a plate fixed to the vertebral bodies in the front with the help of screws. This structure holds itself till the period when the body heals the fusion mass or the space between the two vertebral bodies. The disc space is also cleaned thoroughly and the endplates of the vertebral bodies freshened and prepared to be ready for fusion.
What are the steps to ensure the nerves are not damaged during the surgery?
Enhanced visualization with the use of magnified glasses or loops or the use of operating microscope along with use of precision instruments including micro instruments allow us to avoid any inadvertent injury to the spinal cord or the nerves during the surgery.
How is bleeding controlled during the surgery?
We use a variety of measures to control bleeding during the surgery, which includes a monopolar cautery, bipolar cautery, SURGIFLO as a hemostatic agent or thrombin-soaked Gelfoam. These measures are usually adequate to control bleeding during the usual course of surgery.
What imaging techniques are used during ACDF surgery to ensure accuracy?
Fluoroscopy or intraoperative x-rays are most commonly used during the procedure for ACDF surgery to maintain and ensure accuracy during the surgery. Occasionally, an intraoperative CT scan can be used if there is suspicion but fluoroscopy is usually adequate for anterior cervical spine surgery.
What are the immediate postoperative steps before leaving the operating room?
Before leaving the operating room, the surgeon ensures that the patient is extubated and able to move all four extremities. They also ensure that the wound is dry and dressed, and there is no safety concern for the patient.
How do surgeons check the placement of implants during the surgery?
The implant placement is ensured to be in an accurate and satisfactory place by direct visualization as well as use of intraoperative fluoroscopy and x-rays in at least two different views.
How effective is ACDF/TDR in relieving symptoms?
ACDF is expected to give benefits from surgery usually starting immediately after the surgery. Pain is the most predictive symptom to get better after an ACDF/TDR surgery. Tingling and numbness can take time. Weakness, if there is any before the surgery, may or may not improve.
What long-term outcome can I expect from ACDF?
Once the fusion has occurred at the ACDF site which usually takes 3 to 6 months, the patient is almost back to normal. There is always the disc degeneration that happens due to ageing which can continue to happen at other levels. The levels adjacent to the ACDF are more susceptible to such degenerative changes and may become symptomatic over time due to the presence of ACDF construct and fusion at that level.
What are the chances of needing a revision surgery?
ACDF at one level has very high success rate while ACDF at multiple levels do have higher risk of implant loosening or nonhealing at one or more levels, which may need revision surgery to stabilize the construct. TDR at one or two levels have a high success rate. It may need revision if the implant loosens and will need conversion to ACDF
Are there any long-term restrictions that I should be aware of?
Once the ACDF/TDR has healed, there are no long-term restrictions after the surgery.
How does ACDF/TDR affect neck flexibility in the long term?
Single level ACDF causes a loss of about 10% of neck range of motion, which is compensated by other levels over time. TDR by virtue of its function to retain the motion essentially does not restrain any Range of motion of the neck.
How long do the implants last?
The implants are usually made out of Titanium or PEEK and they are there forever. The allograft which can be used as a spacer or filling the spacer usually gets absorbed and replaced by patient’s own bone.
What are the typical long-term pain management strategies?
Pain management is relatively easier after an ACDF surgery as the pain requirement is less. Patients are allowed to take narcotic medication for the initial 1 to 2 weeks as needed. Tylenol can be used to supplement the medications. After 2 to 3 weeks, patient can also take anti-inflammatory medications as needed.
Can I engage in sports after recovering from ACDF/TDR?
Patients who undergo ACDF/TDR can usually go back to their sports at the previous level once complete healing has happened.
How often should I follow up with my surgeon years after the surgery?
We prefer the patient to follow up on yearly basis once the surgery is done and the healing has happened.
What does rehabilitation involve after ACDF surgery?
The rehabilitation after an ACDF surgery is an easy and smooth recovery with usual activities of daily living. It does not involve going to physical therapy especially for the first 2 to 4 weeks. Most of the patients after ACDF do not need to go therapy for the cervical spine in the acute postoperative period.
How soon can I start physical therapy?
Most patients who undergo ACDF do not need to start physical therapy for their neck for the first 4 to 6 weeks. At 4 to 6 weeks, the physician decides if the patient needs therapy or not.
What are the goals of physical therapy post ACDF?
Physical therapy post ACDF usually at home involves doing activities of daily living and recovering the usual pain free range of motion and strength in the muscles of the cervical spine.
Are there exercises I should avoid after ACDF?
Immediately after ACDF surgery, patients are asked not to carry out lifting, bending, or twisting movements to avoid extra stress on the implant construct in the ACDF.
How long does it typically take to regain normal range of motion?
It takes about 4 to 6 weeks to optimize and regain usual range of motion after ACDF surgery.
What equipment might I need at home during recovery?
There is no usual specific equipment that are needed for ACDF recovery. The physical therapy and rehabilitation post ACDF usually involves activities of daily living and neck range of motion exercises with no excessive bending, twisting, or lifting.
What are the benefits of wearing a collar?
A cervical collar is for protection and immobilization of the neck. It helps reducing stresses on the implant construct post ACDF.
Can I do physical therapy exercises at home?
As the therapies are attended only 2 to 3 days a week, patient should carry out those exercises at home also for the rest of the other days so as to continually keep improving.
How often should I attend physical therapy sessions?
Physical therapy sessions should be attended 2 to 3 times a week for a period as long as it takes for recovery.
What are the signs that physical therapy is working?
Progressive improvement in range of motion as well as strength and decrease in pain and other symptoms are the signs that suggest that the physical therapy is working.
What is the typical recovery time after ACDF/TDA?
Recovery time after ACDF/TDA like any other surgery varies from patient to patient. It also depends on preoperative symptoms and presentation. A typical postoperative recovery can take 6 to 12 weeks for a patient to almost completely recover. If the surgery is done at multiple levels, it can take longer time to recover and can have pain in their shoulder or in their throat for a longer time than a single level surgery.
What are the signs of complications after ACDF/TDA?
ACDF/TDA has a low complication profile in general. The plane that is developed to do the surgery is between large vessels and the food and the windpipe. Injury to any of these can create a complication which may need immediate management. These complications are rare to happen. The patient can also develop other complication like injury to the nerve of the vocal cord leading to medium to long-term hoarseness, wound dehiscence. Infection in ACDF/TDA is very unusual and may signify an injury to the esophagus or the food pipe unless ruled out.
What symptoms are common after ACDF/TDA surgery?
Patients after ACDF/TDA surgery can complain of pain in both shoulders as they are taped down to the table. They can also have hoarseness of voice and difficulty eating food for a short period of time. These symptoms usually get better in the next 3 to 5 days. If these symptoms are not getting better, they should reach out to their operating surgeon who can prescribe them some medications for an early recovery.
How long do I need to stay in the hospital?
Patients after a one level ACDF may be able to go home the same day, if not, the next day morning. Patients who undergo surgery at multiple levels may have to stay in the hospital for 1 to 3 days before they can be sent home.
When can I start eating and drinking after ACDF/TDA?
Patients are allowed to have food after surgery but considering that the food pipe may be swollen, they are asked to take soft food to start with. Once they are able to tolerate soft food, they are asked to thicken the consistency of the food till they get on to their normal diet.
What kind of follow-up is required post surgery?
Patients are usually seen at 2 weeks, 6 weeks, 12 weeks, and then every 12 weeks after that. Patients may need to do x-rays at every follow-up.
What activity should be avoided after ACDF/TDA?
Patients should not be driving immediately after surgery especially if they are on pain medications. They should not be lifting, pulling, or pushing heavy objects. They are allowed to do usual activities of daily living.
How can I care for the surgical site at home?
The surgical site usually has absorbable sutures and with possibly a glue or strips over it. The dressing is usually removed in 3 days and patient is allowed to take showers. The glue or the strips should be allowed to stay there till they peel off by itself. The wound should be kept dry. Patient should not be taking bath. Once 2 to 3 weeks have passed after the surgery, the wound should be taken care as usual and a gentle massage can be done over the incision site.
When can I return to work after ACDF/TDA surgery?
Return to work after an ACDF/TDA surgery depends on patients’ profile as well as the type of work they do and the levels of surgery done. Patients who are in a managerial position or desk job may be able to return to work in 2 weeks while patients who are in heavy manual work may take 6 to 12 weeks to return to work.
What tests are required before undergoing ACDF/TDA?
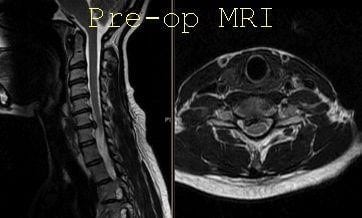
Usual imaging studies including x-ray and MRI are required before confirming and discussing the need for ACDF/TDA surgery. If the MRI is not possible due to contraindications, then a CT myelogram may be needed. Other imaging studies that are helpful and may be done include CT scan of the cervical spine, nerve conduction study and electromyography of both upper extremities. The CT scan helps to evaluate the bony structures as well as the path of the vertebral artery. On the contrary, MRI helps to look at the soft tissue structures including a disc, nerve root as well as the spinal cord and to see if there is any swelling or degeneration to the spinal cord which can alter the prognosis of the disease process. If the patient is undergoing a revision or a second time surgery on the front of the neck (ACDF/TDA), then they should undergo an ENT consult to find out that their vocal cords are working fine. This helps in deciding the side to approach the patient’s neck.
How do I know if I am a good candidate for ACDF/TDA surgery?
Patients who have pain going down into their arms in a specific region (dermatome) on one or both sides (Cervical Radiculopathy) or patients who have balance problems and weakness either in the arms or legs (Cervical Myelopathy) and have imaging findings including x-ray and MRI findings which correlate with such symptoms are candidate for surgeries on the cervical spine. These surgeries can be done either from the front or the back depending on the type of pathology they have. The spine surgeon taking care of the patient is able to discern what type of surgery is best for the patient and should be able to discuss with the patient about it. If the compression on the spinal cord or the nerve is from the front of the neck, ACDF/TDA usually should be able to take care of it. Occasionally, if the compression is due to buckling of the ligament on the back of the spinal cord, then also ACDF/TDA can be helpful. In some circumstances, a surgery from the back of the neck that is posterior spinal fusion with decompression may be needed with or without ACDF surgery.
How should I prepare for ACDF/TDA surgery?
Preparation for ACDF/TDA surgery is as usual as for any other surgery. You should stop any supplements two to three weeks ahead of surgery. You should stop anti-inflammatory medication like Aleve or Advil five days before the surgery. The blood thinners including aspirin should be stopped five days before the surgery or as per the recommendation by the patient’s primary care physician or cardiologist. Patients may be given specific instructions regarding taking care of the skin before the surgery. Patient should not wear any jewellery to the hospital. Patients usually have to undergo a free surgical testing before the surgery, which will help understand their health status. If they have any preexisting medical disease, it should be optimized under care of their primary care physician and any other specialist that they usually see.
Are there any lifestyle changes I need to make after PLIF surgery?
Patients are often advised to avoid heavy lifting, high-impact activities, and smoking, as these can affect the healing process. A healthy diet and regular exercise are encouraged.
What should I tell my doctor about my health history before ACDF/TDA?
Patient should inform in detail all their past medical history, which includes any chronic diseases they have or any diseases for which they are taking any medications at present, most importantly are medications like blood thinners that can affect the surgery. Also, the new weight loss medications should be informed as they alter the effect of anesthesia and they need to be stopped prior to surgery.
Are there any medications I should avoid before ACDF/TDA?
Patient should stop all anti-inflammatory medications five days prior to surgery. Patient should also stop weight loss medications as well as blood thinners prior to surgery on recommendations of their treating physicians. Patient should inform of all the medications that they are taking to the doctor as well as the presurgical testing team. They should stop all supplements two to three weeks prior to surgery.
Can lifestyle factors like smoking affect the outcome of ACDF/TDA surgery?
Smoking or use of nicotine patches can lead to high risk of complications including wound dehiscence, infection as well as nonhealing of the fusion site leading to failure of ACDF. Patients are strongly suggested to stop any smoking and even nicotine patches prior to surgery and not to smoke for at least two to four weeks after the surgery. It can also cause issues with soft tissue healing leading to high wound complication rates.
What are typical preoperative nutritional recommendations?
Patient should be having healthy diet before and after the surgery. They should not take any nutritional supplements two to three weeks prior to surgery as these nutritional supplements may alter the hemodynamics and lead to increased risk during the surgery.
What preoperative exercises might be beneficial?
Patient should be regularly exercising as usual. There are no specific exercises before the surgery. Patient should stay active and carry out activities what they usually are able to perform before the surgery.
Are there any alternative treatments to consider before opting for ACDF/TDA?
Patient should usually try all nonoperative management including physical therapy, medication, injections so as to see if they can help and avoid surgery. if nonoperative management fails and patient has imaging studies suggesting pathology which correlates with the symptoms, then ACDF/TDA or any other surgery that is recommended by the surgeon may be required.
What is ACDF surgery?
ACDF stands for anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. It involves an approach to the front of the neck and reach the discs in the cervical spine, which are cleaned up thereby removing pressure from the nerves and replacing them with a cage filled with bone graft followed by application of plate and screws. It can be done at one or multiple levels.
Who typically needs ACDF surgery?
Patients who have cervical radiculopathy or myelopathy may need ACDF surgery. Cervical radiculopathy means radiating pain into one or both arms, which may be associated with tingling, numbness, or weakness also. Cervical myelopathy means compression of the spinal cord causing weakness into the arms or legs with involvement of balance and/or bowel and bladder functions.
What are the main goals of ACDF surgery?
The main goal of ACDF surgery is to decompress and remove pressure from over the nerve roots as well as the spinal cord from the front of the spine. This takes away pressure and helps to recover the function of the nerve as well as spinal cord.
What symptoms does ACDF surgery address?
ACDF surgery helps in resolution of cervical radiculopathy or cervical myelopathy. Cervical radiculopathy means radiating pain into one or both arms, which may or may not be associated with tingling, numbness, or weakness. Cervical myelopathy means compression of the spinal cord causing weakness in arms or legs with or without balance and/or bowel and bladder function involvement.
How is ACDF surgery performed?
ACDF surgery is performed from the front of the neck. Usually, a transverse incision is given into one of the creases of the neck making it cosmetically acceptable after healing. The incision is usually on one side of the neck. After the skin is incised, the muscles are incised or retracted to develop a plane to reach the front of the spinal column. Once the spinal column is reached, the level is checked with x-rays and retraction is applied in all four directions protecting and retracting the vital structures and vessels. After that, the disc space is cleaned up and all the bony osteophytes as well as endplate cartilage is removed.
Once the back of the vertebral body is reached where the pressure on the spinal cord and nerve root is there, the access of disc as well as osteophytes are removed allowing decompression of spinal cord and nerve root into the neural foramina. Once decompression is confirmed and hemostasis is achieved, the disc is filled with appropriately sized spacer, which can be made out of cadaveric bone or PEEK or Titanium.
These cages are usually empty in between which is packed with the patient’s local bone harvesting while cleaning and mixed with cadaveric bone to allow stimulation for bone healing. Once the cage is put in and confirmed on x-rays, a plate is applied on the front of the spine and fixed with screws in the bodies above and below. This surgery can be done on one or more than one level.
What type of tools and implants are used during ACDF?
There are microsurgical tools that are required for performing the surgery apart from usual spine surgery instruments. We may also use a high-speed drill bit to clean up the osteophytes as well as prepare the endplates for fusion. Implants are usually made of Titanium but can also be made of PEEK especially for the cage. We use patient’s local bone harvesting during the preparation of the endplates, which may also be mixed with cadaveric bone grafts to allow stimulation for healing. The cages are usually stabilized with the use of screws, plates and screws, or sometimes plates.
How long does an ACDF surgery typically take?
A one level ACDF surgery usually takes one and a half hours of surgical time. There are certain other things to be done before the start of surgery as well as after the surgery, which can take a little more time. Multiple level surgeries can take extra time by about 30 minutes to 45 minutes per level.
What defines a minimally invasive ACDF surgery?
Though ACDF surgery is done through an open incision, it can be defined as minimally invasive because the muscles are retracted and minimal soft tissue damage is done during the surgery. The blood loss is also minimal and the recovery is very fast. Patients who undergo one level surgery can go home the same day. Patients who undergo multiple level ACDF surgery usually go home in one or two days.
How is ACDF different from posterior cervical fusion?
ACDF involves decompressing the spinal cord and nerve roots from the front of the spine for compressions which are in that area. Posterior cervical fusion involves decompressing the cervical spine from the back for compression from the back of the spine. ACDF surgery has minimal blood loss as compared to posterior cervical fusion. The recovery is also faster and patient has minimal pain after ACDF surgery as compared to posterior cervical fusion. The complication rates are also low including infection and wound dehiscence as compared to posterior cervical fusion. Overall, ACDF surgery is recommended over posterior cervical fusion if it can take care of the pathology. Sometimes, the cervical spine pathology is such that a posterior cervical spine fusion is mandatory, which may be done isolated or in combination with an anterior cervical spine fusion surgery.
What are the risks of not undergoing ACDF when recommended?
ACDF surgeries are usually elective and if required can be delayed on patient’s or surgeon’s convenience. Occasionally, they can be urgent especially if patient is losing power in his muscles in which case a delay can be detrimental. If the patient’s symptoms are worsening or not improving with nonoperative measures, then ACDF may be required to help improve the quality of life and symptoms for the patient.
How long does the ACDF surgery usually take?
ACDF surgery typically takes between 1 to 3 hours, depending on the number of discs being treated and the complexity of the case.
Will I need to wear a neck brace after the surgery?
Yes, most patients are advised to wear a neck brace for a few weeks post-surgery to support the neck and ensure proper healing
How soon can I return to work after ACDF surgery?
The timeline for returning to work varies, but many patients can return to a desk job within 4 to 6 weeks. Physically demanding jobs may require a longer recovery period.
What type of anesthesia is used during ACDF?
ACDF is performed under general anesthesia, meaning you will be asleep and pain-free during the procedure.
Are there any dietary restrictions after ACDF surgery?
You may need to start with a soft diet if you experience throat discomfort. Gradually, you can return to your normal diet as tolerated.
How is the bone graft material chosen for ACDF?
Bone graft materials can be autograft (your own bone), allograft (donor bone), or synthetic. The choice depends on individual patient factors and surgeon preference.
What are the signs of a successful fusion after ACDF?
A successful fusion typically results in stable neck movement without pain, and imaging studies like X-rays or CT scans will show bone growth across the fused segment.
Can ACDF be performed on multiple levels of the cervical spine?
Yes, ACDF can be performed on multiple levels, though multi-level fusions may have a longer recovery period and increased risk of complications.
Will I lose any range of motion in my neck after ACDF?
Some loss of range of motion is expected, especially if multiple levels are fused. However, most patients find the reduction in pain outweighs this limitation.
Can ACDF be done as an outpatient procedure?
In some cases, ACDF can be performed on an outpatient basis, but this depends on the patient’s overall health and the extent of the surgery.
How should I sleep after ACDF surgery?
It’s often recommended to sleep with your head elevated using pillows or a recliner to reduce swelling and discomfort.
Are there any long-term activity restrictions after ACDF?
Once fully healed, most patients can resume normal activities, but it’s wise to avoid high-impact sports and heavy lifting that could strain the neck.
What should I do if I experience severe pain after ACDF surgery?
Severe pain should be reported to your surgeon immediately, as it could indicate complications such as infection or issues with the fusion.
Will I need physical therapy after ACDF?
Yes, physical therapy is often recommended to help restore strength and flexibility in the neck and shoulders.
How does smoking affect the success of ACDF surgery?
Smoking significantly increases the risk of non-fusion and other complications, so it’s strongly advised to quit smoking before and after surgery.
Can I travel by air after ACDF surgery?
It’s usually safe to fly a few weeks after surgery, but you should discuss your travel plans with your surgeon to ensure it’s appropriate for your recovery stage.
What are the alternatives to ACDF surgery?
Alternatives include non-surgical treatments like physical therapy, medications, and less invasive surgical options like cervical disc replacement.
How can I prepare for ACDF surgery?
Preparation includes stopping certain medications, arranging for post-surgery care, and following pre-operative instructions given by your surgeon.
Will I have a visible scar after ACDF surgery?
The incision is made in a natural skin crease, which helps minimize the visibility of the scar over time.
What is the success rate of ACDF surgery?
ACDF has a high success rate, with over 90% of patients experiencing significant relief from their symptoms.
How often should I follow up with my surgeon after ACDF?
Follow-up visits are typically scheduled at 2 weeks, 6 weeks, 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year post-surgery to monitor healing and fusion progress.
Can ACDF be performed on older adults?
Yes, ACDF can be safely performed on older adults, although they may have a slightly higher risk of complications.
What type of imaging is used to diagnose issues needing ACDF?
Diagnosis typically involves X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to assess the condition of the cervical spine and discs.
How do I know if I am a candidate for ACDF?
You may be a candidate if you have persistent neck pain, arm pain, or neurological symptoms that haven’t responded to non-surgical treatments.
What is the typical hospital stay after ACDF surgery?
Most patients stay in the hospital for 1 to 2 days after ACDF surgery for monitoring and initial recovery.
What are the typical long-term pain management strategies?
Pain management is relatively easier after an ACDF/TDR surgery as the pain requirement is less. Patients are allowed to take narcotic medication for the initial 1 to 2 weeks as needed. Tylenol can be used to supplement the medications. After 2 to 3 weeks, patients can also take anti-inflammatory medications as needed after ACDF surgery. Patients are allowed anti-inflammatory medications sooner after a disc replacement surgery as there is no fusion involved. Anti-inflammatory mediations are known to delay bone healing.
What long-term outcome can I expect from TDR?
Once the implant settles itself into the bone of the endplates with ingrowth into the artificial disc which usually takes 3 to 6 months, the patient is almost back to normal. There is always the disc degeneration that happens due to ageing which can continue to happen at other levels. The levels adjacent to the TDR are less susceptible to such degenerative changes as compared to ACDF but may become symptomatic over time due to the natural progression of the degenerative disease process.
How does ACDF vary for older patients?
ACDF is most commonly done for degenerative disc disease, which is a commoner condition in older population than younger. As the patient gets old, the body physiology changes and any surgery becomes a moderate to high-risk surgery. The physician and the patient have to discuss the risks and the benefits of the surgery to come to a decision if they would like to go forward with the surgery or not. With regards to specific concerns, old age does cause delayed healing which may lead to nonhealing also. Also, the soft tissue healing is slow down and certain tissue are more friable than being a younger adult patient leading to a higher risk of complications including bleeding, dural tear, nonunion or nonhealing, subsidence of the cage among others. Also, if a patient of the older population has neurological deficit, the chances of them recovering is lower than a younger adult. Patients of younger population also are at higher risk with regards to anesthesia as well as postop recovery and rehabilitation.
How is ACDF approach differently for patients with multiple health issues?
Patients with multiple health issues need to be optimized medically before the surgery. If needed, they need to see their primary care doctor as well as other subspecialists that they regularly see as well as the presurgical team. If a new health condition is diagnosed, then they may need to undergo further workup and may need to see another subspecialist with an aim to optimize their health condition before the surgery. The patient’s medications also need to be managed and certain medications need to be stopped before the surgery to decrease the complications from anesthesia and surgery and allow recovery in the postop period.
Are there specific considerations for athletes undergoing ACDF?
There are no specific considerations for athletes who undergo ACDF. In the first place, if the cervical pathology can be managed without a fusion surgery, like by utilizing foraminotomy surgery hence avoiding a fusion surgery can be better for an athlete. Also, if he is a younger patient, we would consider an option of total disc arthroplasty rather than an ACDF to allow retaining movement at the disc space.
What are the gender specific considerations in ACDF?
There are no gender specific concerns in ACDF. The ACDF is done with the same approach and in the same way for either gender. We do try to put the skin incision along one of the neck creases for both genders so as to make it cosmetically more acceptable.
What genetic factors could influence the success of ACDF?
ACDF is inherently a very successful surgery with excellent outcomes. Genetic conditions which hamper or impair the immune system can lead to high risk of complications including infection and nonhealing. Also, patients who have congenital spinal stenosis may need another surgery from the back of the spine to completely relieve the pressure on the spinal cord or the nerve roots. Patients with any genetic conditions which may alter the surgical course need to be optimized, if possible, with medications before the surgery.
How does body weight impact the risk and outcomes of ACDF?
An increased body weight which also means increased BMI does increase risk of complication in any surgery including ACDF. The incidents of wound drainage are higher in patients with increased weight. The chances of a patient with increased weight having other medical problems are higher which also increases the risks of complication as discussed above. The surgery, if well indicated, can still be carried out with safe practices with excellent results.
How does prior neck surgery affect ACDF planning and outcome?
A previous neck surgery makes an ACDF a tough surgery due to the approach to the anterior cervical spine. If the patient had an extensive neck surgery previously for any reason, which leads to scar formation on either side of the neck that is the right and the left side of the neck, then it is better to avoid an ACDF surgery. Occasionally, due to the cervical pathology, it may be necessary to approach the cervical spine from the front in which case we may have to meticulously dissect the soft tissue and protect the vital structures. Rarely, we may need an ENT surgery to help approach the anterior spine. If the patient had an ACDF surgery in the past, then we can approach the neck from either the same side or the other side, approach to the ACDF also depends on the integrity of the nerve supplying the vocal cords. To find that out, the patient is sent for an ENT consult to look for mobility of the vocal cords. The patient may have an asymptomatic paralysis of vocal cord which can be diagnosed by a direct laryngoscopy by the ENT surgery. If we find that the patient has a vocal cord paralysis on the side where the previous ACDF surgery was approached, then we do the surgery from the same side and do not approach the neck from the other side fearing that if the nerve on the other side is also injured inadvertently then the patient may have high risk of respiratory complications.
What are the special considerations for patients with osteoporosis?
Patients who are diagnosed with osteoporosis before the surgery are managed with medications to optimize their bone health and improve their bone quality. If the surgery is still indicated, meticulous and efficient method is used to keep the integrity of the endplates, at the same time preparing them for fusion. Different implants may be used for such surgery. Occasionally, patients with osteoporosis may need a surgery from the back of the neck to increase the stabilization at the level so that collapse can be avoided and healing can happen
How does diabetes affect ACDF surgery and recovery?
Patients with diabetes have poor immune system and are at higher risk of infection as well as delayed or nonhealing. Optimization of blood sugar in the previous three months can help to mitigate some of these risks. Patients are encouraged to keep the control of blood sugar at a strict level in the perioperative period.
Are there specific concerns of patients with autoimmune disorders?
Patients with autoimmune disorders, who are on medications, have poor immune response due to the medication effect. They are at higher risk of infection as well as poor healing of the soft tissue as well as bone. Their health condition needs to be optimized and coordinated with their primary care doctor and rheumatologist and autoimmune expert, and patients are informed of the higher risks during and after the surgery.
How can complications be minimized?
With the use of magnified vision by using loops or operating microscope, the visualization is enhanced and it helps in decreasing the complications. Also, using appropriate instruments and retraction and the use of good team helps in minimizing the complications.
What are the signs of infection after ACDF/TDR?
Redness, swelling, discharge from the incision site, pain in the neck or in the upper chest, fever, chills, increased heart rate are few of many signs of infection after ACDF/TDR. Patient should be taken to the emergency room or informed to the doctor immediately when such things happen.
What are the most common complications of ACDF/TDR surgery?
ACDF/TDR surgery is a relatively safe surgery with a very low rate of complications. Most common complaints of patients after an Anterior cervical surgery (ACDF or TDR) are related to shoulder pain due to positioning and positioning and hoarseness of voice due to retraction. These complaints usually improve in the next 3-5 days. Occasionally patients may need medications for it. They can have dysphonia or hoarseness of voice due to retraction as well as the endotracheal tube. We tend to mitigate this by deflating and reinflating the endotracheal tube cuff so as to decrease the pressure on the vocal cords. Rarely, the recurrent laryngeal nerve, the nerve supplying the vocal cords may get stretched or pressed, in such cases patients may develop a short-term hoarseness of voice for about 4 to 6 months. This hoarseness of voice can be managed by intervention with an ENT doctor. Patients can have dysphagia or difficulty in swallowing, which gets better in the next few days or weeks. The other and usually rare complications can include wound dehiscence, infection, injury to large vessel or food pipe or windpipe, injury to the nerve supplying the vocal cord, injury to the nerve roots or the spinal cord, bleeding among others. Considering the use of magnified vision with the use of loops or microscopes, these incidences are very far and few. Not being able to heal and need for more surgery is also a complication of these surgeries.
What are the risks of spinal cord injury after ACDF/TDR?
Considering that we use magnified vision by using loops or operating microscope, the risk of spinal cord injury after ACDF/TDR is minimal to rare. Sometimes patient may have injury to the spinal cord preexisting due to the arthritis or the disc herniation showing a swelling in the spinal cord on the MRI before the surgery. Decompressing such spinal cord can possibly lead to healing of this lesion with some to full recovery of the symptoms.
What are the risks associated with anesthesia in ACDF/TDR?
Risks of anesthesia in ACDF are the usual as with any other surgery.
How are blood clots prevented during and after ACDF/TDR?
We use sequential compression devices on both calf muscles, calf area to keep the blood pumping from the legs while the patient is in the surgery or after surgery when resting. Patients are encouraged to walk around in the postoperative period which also allows to decrease the risk. Patients are started on anticoagulation prophylaxis if they are high-risk in the postop period once the risk for bleeding is minimized.
What should I do if I experience severe pain after the surgery?
Severe pain is unusual after an ACDF/TDR surgery. Patients are provided with pain medications. If the pain is not controlled with pain medications and is worsening, the patient should contact their doctor. If the doctor is unreachable, then the patient should visit the emergency room to get checked out and to rule out any infection or any other such complication.
What are the risks of nonunion or failed fusion?
The risk of nonunion is very low after a single level ACDF/TDR. If multiple levels are done, then the risk may increase. We use multiple steps to mitigate this risk by doing a good endplate preparation as well as use of local bone graft and allograft to stimulate stimulation with a good fixation to keep the rate low.
What are the implications of hardware failure?
How are dural tears handled during surgery?
Dural tears are rare during an ACDF/TDR surgery. If it is a small rent, then it can usually be packed and sealed with an artificial membrane and sealant. If the tear is big, then we may have to make a bigger cut through the bone to allow repair of the hole with sutures followed by sealing it with a membrane on the top and sealant.
How is the cervical area accessed during the surgery?
Traditionally, cervical spine can be accessed either from the front or the back. The surgery from the front is called anterior cervical discectomy or corpectomy, which is usually associated with fusion. Also, the surgery from the back is called posterior cervical approach and surgeries like posterior cervical laminectomy and fusion or laminoplasty or foraminotomies can be done through that approach. In anterior cervical approach, the skin is usually cut in a transverse manner along a skin crease which is cosmetically acceptable and a plane is developed between the throat muscles and the sternocleidomastoid muscle to reach the anterior part of the front of the cervical spine. This is relatively bloodless surgery with fast recovery and recuperation. Posterior cervical spine surgery is done with a vertical incision along the midline splitting the muscles to reach the back of the cervical spine. Posterior spinal approach is associated with a little more blood loss as compared to the anterior approach and has higher risks and complications, which include wound dehiscence, infection among others.
What type of anesthesia is used during ACDF?
General anesthesia is the usual type of anesthesia we use during ACDF in which a tube is passed into the windpipe or trachea of the patient and the anesthesia controls the ventilation of the lungs.
How are affected cervical discs removed?
The affected cervical discs are removed with the use of a variety of instruments which include a plate, curettes, pituitary rongeurs, Kerrison rongeurs. Various sized instruments are used to allow a microdissection and removal of the disc while at the same time avoiding any injury to the spinal cord or the nerve and protecting the integrity of the spine. The visualization is usually done with the use of specialized glasses which are magnified to 2.5 to 3.5 times or with the use of an operating microscope.
What materials are used for spinal fusion?
The spinal fusion for anterior cervical spine approach or ACDF uses interbody cage between the two vertebral bodies in the disc space which can be made up of fibular cadaveric bone graft or PEEK cage or a Titanium cage usually. This is supported with a plate in front of the spine, which is usually made of titanium and fixed with titanium screws.
How is fusion material secured?
To allow fusion to happen between two cervical vertebral bodies, we usually pack the space between them with a spacer which can be of an allograft, autograft, PEEK, or Titanium, which is packed with bone either from patient’s body or from a cadaver or a mixture of the two and the structure is held together with a plate fixed to the vertebral bodies in the front with the help of screws. This structure holds itself till the period when the body heals the fusion mass or the space between the two vertebral bodies. The disc space is also cleaned thoroughly and the endplates of the vertebral bodies freshened and prepared to be ready for fusion.
What are the steps to ensure the nerves are not damaged during the surgery?
Enhanced visualization with the use of magnified glasses or loops or the use of operating microscope along with use of precision instruments including micro instruments allow us to avoid any inadvertent injury to the spinal cord or the nerves during the surgery.
How is bleeding controlled during the surgery?
We use a variety of measures to control bleeding during the surgery, which includes a monopolar cautery, bipolar cautery, SURGIFLO as a hemostatic agent or thrombin-soaked Gelfoam. These measures are usually adequate to control bleeding during the usual course of surgery.
What imaging techniques are used during ACDF surgery to ensure accuracy?
Fluoroscopy or intraoperative x-rays are most commonly used during the procedure for ACDF surgery to maintain and ensure accuracy during the surgery. Occasionally, an intraoperative CT scan can be used if there is suspicion but fluoroscopy is usually adequate for anterior cervical spine surgery.
What are the immediate postoperative steps before leaving the operating room?
Before leaving the operating room, the surgeon ensures that the patient is extubated and able to move all four extremities. They also ensure that the wound is dry and dressed, and there is no safety concern for the patient.
How do surgeons check the placement of implants during the surgery?
The implant placement is ensured to be in an accurate and satisfactory place by direct visualization as well as use of intraoperative fluoroscopy and x-rays in at least two different views.
What long-term outcome can I expect from ACDF?
Once the fusion has occurred at the ACDF site which usually takes 3 to 6 months, the patient is almost back to normal. There is always the disc degeneration that happens due to ageing which can continue to happen at other levels. The levels adjacent to the ACDF are more susceptible to such degenerative changes and may become symptomatic over time due to the presence of ACDF construct and fusion at that level.
How effective is ACDF/TDR in relieving symptoms?
ACDF is expected to give benefits from surgery usually starting immediately after the surgery. Pain is the most predictive symptom to get better after an ACDF/TDR surgery. Tingling and numbness can take time. Weakness, if there is any before the surgery, may or may not improve.
What are the chances of needing a revision surgery?
ACDF at one level has very high success rate while ACDF at multiple levels do have higher risk of implant loosening or nonhealing at one or more levels, which may need revision surgery to stabilize the construct. TDR at one or two levels have a high success rate. It may need revision if the implant loosens and will need conversion to ACDF
Are there any long-term restrictions that I should be aware of?
Once the ACDF/TDR has healed, there are no long-term restrictions after the surgery.
How does ACDF/TDR affect neck flexibility in the long term?
Single level ACDF causes a loss of about 10% of neck range of motion, which is compensated by other levels over time. TDR by virtue of its function to retain the motion essentially does not restrain any Range of motion of the neck.
How long do the implants last?
The implants are usually made out of Titanium or PEEK and they are there forever. The allograft which can be used as a spacer or filling the spacer usually gets absorbed and replaced by patient’s own bone.
What are the typical long-term pain management strategies?
Pain management is relatively easier after an ACDF surgery as the pain requirement is less. Patients are allowed to take narcotic medication for the initial 1 to 2 weeks as needed. Tylenol can be used to supplement the medications. After 2 to 3 weeks, patient can also take anti-inflammatory medications as needed.
Can I engage in sports after recovering from ACDF/TDR?
Patients who undergo ACDF/TDR can usually go back to their sports at the previous level once complete healing has happened.
How often should I follow up with my surgeon years after the surgery?
We prefer the patient to follow up on yearly basis once the surgery is done and the healing has happened.
What does rehabilitation involve after ACDF surgery?
The rehabilitation after an ACDF surgery is an easy and smooth recovery with usual activities of daily living. It does not involve going to physical therapy especially for the first 2 to 4 weeks. Most of the patients after ACDF do not need to go therapy for the cervical spine in the acute postoperative period.
How soon can I start physical therapy?
Most patients who undergo ACDF do not need to start physical therapy for their neck for the first 4 to 6 weeks. At 4 to 6 weeks, the physician decides if the patient needs therapy or not.
What are the goals of physical therapy post ACDF?
Physical therapy post ACDF usually at home involves doing activities of daily living and recovering the usual pain free range of motion and strength in the muscles of the cervical spine.
Are there exercises I should avoid after ACDF?
Immediately after ACDF surgery, patients are asked not to carry out lifting, bending, or twisting movements to avoid extra stress on the implant construct in the ACDF.
How long does it typically take to regain normal range of motion?
It takes about 4 to 6 weeks to optimize and regain usual range of motion after ACDF surgery.
What equipment might I need at home during recovery?
There is no usual specific equipment that are needed for ACDF recovery. The physical therapy and rehabilitation post ACDF usually involves activities of daily living and neck range of motion exercises with no excessive bending, twisting, or lifting.
What are the benefits of wearing a collar?
A cervical collar is for protection and immobilization of the neck. It helps reducing stresses on the implant construct post ACDF.
Can I do physical therapy exercises at home?
As the therapies are attended only 2 to 3 days a week, patient should carry out those exercises at home also for the rest of the other days so as to continually keep improving.
How often should I attend physical therapy sessions?
Physical therapy sessions should be attended 2 to 3 times a week for a period as long as it takes for recovery.
What are the signs that physical therapy is working?
Progressive improvement in range of motion as well as strength and decrease in pain and other symptoms are the signs that suggest that the physical therapy is working.
What is the typical recovery time after ACDF/TDA?
Recovery time after ACDF/TDA like any other surgery varies from patient to patient. It also depends on preoperative symptoms and presentation. A typical postoperative recovery can take 6 to 12 weeks for a patient to almost completely recover. If the surgery is done at multiple levels, it can take longer time to recover and can have pain in their shoulder or in their throat for a longer time than a single level surgery.
What are the signs of complications after ACDF/TDA?
ACDF/TDA has a low complication profile in general. The plane that is developed to do the surgery is between large vessels and the food and the windpipe. Injury to any of these can create a complication which may need immediate management. These complications are rare to happen. The patient can also develop other complication like injury to the nerve of the vocal cord leading to medium to long-term hoarseness, wound dehiscence. Infection in ACDF/TDA is very unusual and may signify an injury to the esophagus or the food pipe unless ruled out.
What symptoms are common after ACDF/TDA surgery?
Patients after ACDF/TDA surgery can complain of pain in both shoulders as they are taped down to the table. They can also have hoarseness of voice and difficulty eating food for a short period of time. These symptoms usually get better in the next 3 to 5 days. If these symptoms are not getting better, they should reach out to their operating surgeon who can prescribe them some medications for an early recovery.
How long do I need to stay in the hospital?
Patients after a one level ACDF may be able to go home the same day, if not, the next day morning. Patients who undergo surgery at multiple levels may have to stay in the hospital for 1 to 3 days before they can be sent home.
When can I start eating and drinking after ACDF/TDA?
Patients are allowed to have food after surgery but considering that the food pipe may be swollen, they are asked to take soft food to start with. Once they are able to tolerate soft food, they are asked to thicken the consistency of the food till they get on to their normal diet.
What kind of follow-up is required post surgery?
Patients are usually seen at 2 weeks, 6 weeks, 12 weeks, and then every 12 weeks after that. Patients may need to do x-rays at every follow-up.
What activity should be avoided after ACDF/TDA?
Patients should not be driving immediately after surgery especially if they are on pain medications. They should not be lifting, pulling, or pushing heavy objects. They are allowed to do usual activities of daily living.
How can I care for the surgical site at home?
The surgical site usually has absorbable sutures and with possibly a glue or strips over it. The dressing is usually removed in 3 days and patient is allowed to take showers. The glue or the strips should be allowed to stay there till they peel off by itself. The wound should be kept dry. Patient should not be taking bath. Once 2 to 3 weeks have passed after the surgery, the wound should be taken care as usual and a gentle massage can be done over the incision site.
When can I return to work after ACDF/TDA surgery?
Return to work after an ACDF/TDA surgery depends on patients’ profile as well as the type of work they do and the levels of surgery done. Patients who are in a managerial position or desk job may be able to return to work in 2 weeks while patients who are in heavy manual work may take 6 to 12 weeks to return to work.
What tests are required before undergoing ACDF/TDA?
Usual imaging studies including x-ray and MRI are required before confirming and discussing the need for ACDF/TDA surgery. If the MRI is not possible due to contraindications, then a CT myelogram may be needed. Other imaging studies that are helpful and may be done include CT scan of the cervical spine, nerve conduction study and electromyography of both upper extremities. The CT scan helps to evaluate the bony structures as well as the path of the vertebral artery. On the contrary, MRI helps to look at the soft tissue structures including a disc, nerve root as well as the spinal cord and to see if there is any swelling or degeneration to the spinal cord which can alter the prognosis of the disease process. If the patient is undergoing a revision or a second time surgery on the front of the neck (ACDF/TDA), then they should undergo an ENT consult to find out that their vocal cords are working fine. This helps in deciding the side to approach the patient’s neck.
How do I know if I am a good candidate for ACDF/TDA surgery?
Patients who have pain going down into their arms in a specific region (dermatome) on one or both sides (Cervical Radiculopathy) or patients who have balance problems and weakness either in the arms or legs (Cervical Myelopathy) and have imaging findings including x-ray and MRI findings which correlate with such symptoms are candidate for surgeries on the cervical spine. These surgeries can be done either from the front or the back depending on the type of pathology they have. The spine surgeon taking care of the patient is able to discern what type of surgery is best for the patient and should be able to discuss with the patient about it. If the compression on the spinal cord or the nerve is from the front of the neck, ACDF/TDA usually should be able to take care of it. Occasionally, if the compression is due to buckling of the ligament on the back of the spinal cord, then also ACDF/TDA can be helpful. In some circumstances, a surgery from the back of the neck that is posterior spinal fusion with decompression may be needed with or without ACDF surgery.
How should I prepare for ACDF/TDA surgery?
Preparation for ACDF/TDA surgery is as usual as for any other surgery. You should stop any supplements two to three weeks ahead of surgery. You should stop anti-inflammatory medication like Aleve or Advil five days before the surgery. The blood thinners including aspirin should be stopped five days before the surgery or as per the recommendation by the patient’s primary care physician or cardiologist. Patients may be given specific instructions regarding taking care of the skin before the surgery. Patient should not wear any jewellery to the hospital. Patients usually have to undergo a free surgical testing before the surgery, which will help understand their health status. If they have any preexisting medical disease, it should be optimized under care of their primary care physician and any other specialist that they usually see.
Are there any lifestyle changes I need to make after PLIF surgery?
Patients are often advised to avoid heavy lifting, high-impact activities, and smoking, as these can affect the healing process. A healthy diet and regular exercise are encouraged.
What should I tell my doctor about my health history before ACDF/TDA?
Patient should inform in detail all their past medical history, which includes any chronic diseases they have or any diseases for which they are taking any medications at present, most importantly are medications like blood thinners that can affect the surgery. Also, the new weight loss medications should be informed as they alter the effect of anesthesia and they need to be stopped prior to surgery.
Are there any medications I should avoid before ACDF/TDA?
Patient should stop all anti-inflammatory medications five days prior to surgery. Patient should also stop weight loss medications as well as blood thinners prior to surgery on recommendations of their treating physicians. Patient should inform of all the medications that they are taking to the doctor as well as the presurgical testing team. They should stop all supplements two to three weeks prior to surgery.
Can lifestyle factors like smoking affect the outcome of ACDF/TDA surgery?
Smoking or use of nicotine patches can lead to high risk of complications including wound dehiscence, infection as well as nonhealing of the fusion site leading to failure of ACDF. Patients are strongly suggested to stop any smoking and even nicotine patches prior to surgery and not to smoke for at least two to four weeks after the surgery. It can also cause issues with soft tissue healing leading to high wound complication rates.
What are typical preoperative nutritional recommendations?
Patient should be having healthy diet before and after the surgery. They should not take any nutritional supplements two to three weeks prior to surgery as these nutritional supplements may alter the hemodynamics and lead to increased risk during the surgery.
What preoperative exercises might be beneficial?
Patient should be regularly exercising as usual. There are no specific exercises before the surgery. Patient should stay active and carry out activities what they usually are able to perform before the surgery.
Are there any alternative treatments to consider before opting for ACDF/TDA?
Patient should usually try all nonoperative management including physical therapy, medication, injections so as to see if they can help and avoid surgery. if nonoperative management fails and patient has imaging studies suggesting pathology which correlates with the symptoms, then ACDF/TDA or any other surgery that is recommended by the surgeon may be required.
What is ACDF surgery?
ACDF stands for anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. It involves an approach to the front of the neck and reach the discs in the cervical spine, which are cleaned up thereby removing pressure from the nerves and replacing them with a cage filled with bone graft followed by application of plate and screws. It can be done at one or multiple levels.
Who typically needs ACDF surgery?
Patients who have cervical radiculopathy or myelopathy may need ACDF surgery. Cervical radiculopathy means radiating pain into one or both arms, which may be associated with tingling, numbness, or weakness also. Cervical myelopathy means compression of the spinal cord causing weakness into the arms or legs with involvement of balance and/or bowel and bladder functions.
What are the main goals of ACDF surgery?
The main goal of ACDF surgery is to decompress and remove pressure from over the nerve roots as well as the spinal cord from the front of the spine. This takes away pressure and helps to recover the function of the nerve as well as spinal cord.
What symptoms does ACDF surgery address?
ACDF surgery helps in resolution of cervical radiculopathy or cervical myelopathy. Cervical radiculopathy means radiating pain into one or both arms, which may or may not be associated with tingling, numbness, or weakness. Cervical myelopathy means compression of the spinal cord causing weakness in arms or legs with or without balance and/or bowel and bladder function involvement.
How is ACDF surgery performed?
ACDF surgery is performed from the front of the neck. Usually, a transverse incision is given into one of the creases of the neck making it cosmetically acceptable after healing. The incision is usually on one side of the neck. After the skin is incised, the muscles are incised or retracted to develop a plane to reach the front of the spinal column. Once the spinal column is reached, the level is checked with x-rays and retraction is applied in all four directions protecting and retracting the vital structures and vessels. After that, the disc space is cleaned up and all the bony osteophytes as well as endplate cartilage is removed.
Once the back of the vertebral body is reached where the pressure on the spinal cord and nerve root is there, the access of disc as well as osteophytes are removed allowing decompression of spinal cord and nerve root into the neural foramina. Once decompression is confirmed and hemostasis is achieved, the disc is filled with appropriately sized spacer, which can be made out of cadaveric bone or PEEK or Titanium.
These cages are usually empty in between which is packed with the patient’s local bone harvesting while cleaning and mixed with cadaveric bone to allow stimulation for bone healing. Once the cage is put in and confirmed on x-rays, a plate is applied on the front of the spine and fixed with screws in the bodies above and below. This surgery can be done on one or more than one level.
How long does an ACDF surgery typically take?
A one level ACDF surgery usually takes one and a half hours of surgical time. There are certain other things to be done before the start of surgery as well as after the surgery, which can take a little more time. Multiple level surgeries can take extra time by about 30 minutes to 45 minutes per level.
What type of tools and implants are used during ACDF?
There are microsurgical tools that are required for performing the surgery apart from usual spine surgery instruments. We may also use a high-speed drill bit to clean up the osteophytes as well as prepare the endplates for fusion. Implants are usually made of Titanium but can also be made of PEEK especially for the cage. We use patient’s local bone harvesting during the preparation of the endplates, which may also be mixed with cadaveric bone grafts to allow stimulation for healing. The cages are usually stabilized with the use of screws, plates and screws, or sometimes plates.
What defines a minimally invasive ACDF surgery?
Though ACDF surgery is done through an open incision, it can be defined as minimally invasive because the muscles are retracted and minimal soft tissue damage is done during the surgery. The blood loss is also minimal and the recovery is very fast. Patients who undergo one level surgery can go home the same day. Patients who undergo multiple level ACDF surgery usually go home in one or two days.
How is ACDF different from posterior cervical fusion?
ACDF involves decompressing the spinal cord and nerve roots from the front of the spine for compressions which are in that area. Posterior cervical fusion involves decompressing the cervical spine from the back for compression from the back of the spine. ACDF surgery has minimal blood loss as compared to posterior cervical fusion. The recovery is also faster and patient has minimal pain after ACDF surgery as compared to posterior cervical fusion. The complication rates are also low including infection and wound dehiscence as compared to posterior cervical fusion. Overall, ACDF surgery is recommended over posterior cervical fusion if it can take care of the pathology. Sometimes, the cervical spine pathology is such that a posterior cervical spine fusion is mandatory, which may be done isolated or in combination with an anterior cervical spine fusion surgery.
What are the risks of not undergoing ACDF when recommended?
ACDF surgeries are usually elective and if required can be delayed on patient’s or surgeon’s convenience. Occasionally, they can be urgent especially if patient is losing power in his muscles in which case a delay can be detrimental. If the patient’s symptoms are worsening or not improving with nonoperative measures, then ACDF may be required to help improve the quality of life and symptoms for the patient.
I am Vedant Vaksha, Fellowship trained Spine, Sports and Arthroscopic Surgeon at Complete Orthopedics. I take care of patients with ailments of the neck, back, shoulder, knee, elbow and ankle. I personally approve this content and have written most of it myself.
Please take a look at my profile page and don't hesitate to come in and talk.